Dysregulation of POPDC1 promotes breast cancer cell migration and proliferation
- PMID: 28954821
- PMCID: PMC5696453
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20171039
Dysregulation of POPDC1 promotes breast cancer cell migration and proliferation
Abstract
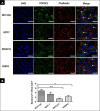
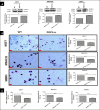
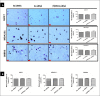
Breast cancer subtypes such as triple-negative that lack the expression of oestrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR) and human epidermal growth factor 2 receptor (HER2), remain poorly clinically managed due to a lack of therapeutic targets. This necessitates identification and validation of novel targets. Suppression of Popeye domain-containing protein 1 (POPDC1) is known to promote tumorigenesis and correlate to poor clinical outcomes in various cancers, and also promotes cardiac and skeletal muscle pathologies. It remains to be established whether POPDC1 is dysregulated in breast cancer, and whether overcoming the dysregulation of POPDC1 could present a potential therapeutic strategy to inhibit breast tumorigenesis. We assessed the potential of POPDC1 as a novel target for inhibiting breast cancer cell migration and proliferation. POPDC1 was significantly suppressed with reduced cell membrane localization in breast cancer cells. Furthermore, functional suppression of POPDC1 promoted breast cancer cell migration and proliferation, which were inhibited by POPDC1 overexpression. Finally, cAMP interacts with POPDC1 and up-regulates its expression in breast cancer cells. These findings suggest that POPDC1 plays a role in breast tumorigenesis and represents a potential therapeutic target or biomarker in breast cancer medicine.
Keywords: POPDC1; breast cancer; cAMP; cell migration; cell proliferation.
© 2017 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
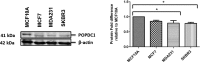



References
-
- Globocan W. Estimated cancer incidence, mortality and prevalence worldwide in 2012. 2014-01-09)[2014-07-01], http://globocan.iarc.fr/Pages/fact_sheets_population.Aspx.
-
- Ferrer-Soler L., Vazquez-Martin A., Brunet J., Menendez J.A., De Llorens R. and Colomer R. (2007) An update of the mechanisms of resistance to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in breast cancer: Gefitinib (iressa™)-induced changes in the expression and nucleo-cytoplasmic trafficking of HER-ligands (review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 20, 3. - PubMed
-
- Normanno N., Luca A.D., Maiello M.R., Campiglio M., Napolitano M., Mancino M. et al. (2006) The MEK/MAPK pathway is involved in the resistance of breast cancer cells to the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib. J. Cell. Physiol. 207, 420–427 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

