A novel intracellular pool of LFA-1 is critical for asymmetric CD8+ T cell activation and differentiation
- PMID: 28954823
- PMCID: PMC5674876
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201609072
A novel intracellular pool of LFA-1 is critical for asymmetric CD8+ T cell activation and differentiation
Abstract
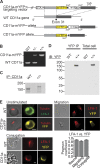
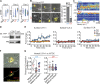
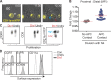
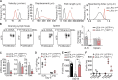
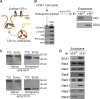
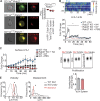
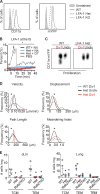
The integrin lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1; CD11a/CD18) is a key T cell adhesion receptor that mediates stable interactions with antigen-presenting cell (APC), as well as chemokine-mediated migration. Using our newly generated CD11a-mYFP knock-in mice, we discovered that naive CD8+ T cells reserve a significant intracellular pool of LFA-1 in the uropod during migration. Intracellular LFA-1 quickly translocated to the cell surface with antigenic stimulus. Importantly, the redistribution of intracellular LFA-1 at the contact with APC was maintained during cell division and led to an unequal inheritance of LFA-1 in divided T cells. The daughter CD8+ T cells with disparate LFA-1 expression showed different patterns of migration on ICAM-1, APC interactions, and tissue retention, as well as altered effector functions. In addition, we identified Rab27 as an important regulator of the intracellular LFA-1 translocation. Collectively, our data demonstrate that an intracellular pool of LFA-1 in naive CD8+ T cells plays a key role in T cell activation and differentiation.
© 2017 Capece et al.
Figures
References
-
- Baker C.M., Comrie W.A., Hyun Y.M., Chung H.L., Fedorchuk C.A., Lim K., Brakebusch C., McGrath J.L., Waugh R.E., Meier-Schellersheim M., and Kim M.. 2012. Opposing roles for RhoH GTPase during T-cell migration and activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 109:10474–10479. 10.1073/pnas.1114214109 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

