Retromer stops beta-arrestin 1-mediated signaling from internalized cannabinoid 2 receptors
- PMID: 28954865
- PMCID: PMC5683765
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E17-03-0198
Retromer stops beta-arrestin 1-mediated signaling from internalized cannabinoid 2 receptors
Abstract
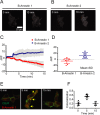
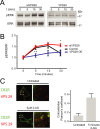
G protein-coupled receptors mediate their complex functions through activation of signaling cascades from receptors localized at the cell surface and endosomal compartments. These signaling pathways are modulated by heterotrimeric G proteins and the scaffold proteins beta-arrestin 1 and 2. However, in contrast to the events occurring at the cell surface, our knowledge of the mechanisms controlling signaling from receptors localized at intracellular compartments is still very limited. Here we sought to investigate the intracellular signaling from cannabinoid 2 receptor (CB2R). First, we show that receptor internalization is required for agonist-induced phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases 1 and 2 (ERK1/2). Then we demonstrate that ERK1/2 activation is mediated by beta-arrestin 1 from receptors localized exclusively at Rab4/5 compartments. Finally, we identify the retromer complex as a gatekeeper, terminating beta-arrestin 1-mediated ERK phosphorylation. These findings extend our understanding of the events controlling signaling from endocytosed receptors and identify the retromer as a modulator of beta-arrestin-mediated signaling from CB2R.
© 2017 Nogueras-Ortiz, Roman-Vendrell, et al. This article is distributed by The American Society for Cell Biology under license from the author(s). Two months after publication it is available to the public under an Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike 3.0 Unported Creative Commons License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0).
Figures





References
-
- Bouaboula M, Poinot-Chazel C, Marchand J, Canat X, Bourrié B, Rinaldi-Carmona M, Calandra B, Le Fur G, Casellas P. Signaling pathway associated with stimulation of CB2 peripheral cannabinoid receptor. Eur J Biochem. 1996;237:704–711. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

