Combinatorial control of gene expression in Aspergillus niger grown on sugar beet pectin
- PMID: 28955038
- PMCID: PMC5617896
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-12362-y
Combinatorial control of gene expression in Aspergillus niger grown on sugar beet pectin
Abstract
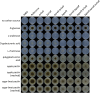
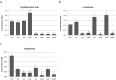
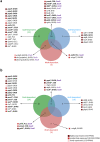
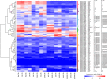
Aspergillus niger produces an arsenal of extracellular enzymes that allow synergistic degradation of plant biomass found in its environment. Pectin is a heteropolymer abundantly present in the primary cell wall of plants. The complex structure of pectin requires multiple enzymes to act together. Production of pectinolytic enzymes in A. niger is highly regulated, which allows flexible and efficient capture of nutrients. So far, three transcriptional activators have been linked to regulation of pectin degradation in A. niger. The L-rhamnose-responsive regulator RhaR controls the production of enzymes that degrade rhamnogalacturonan-I. The L-arabinose-responsive regulator AraR controls the production of enzymes that decompose the arabinan and arabinogalactan side chains of rhamnogalacturonan-II. The D-galacturonic acid-responsive regulator GaaR controls the production of enzymes that act on the polygalacturonic acid backbone of pectin. This project aims to better understand how RhaR, AraR and GaaR co-regulate pectin degradation. For that reason, we constructed single, double and triple disruptant strains of these regulators and analyzed their growth phenotype and pectinolytic gene expression in A. niger grown on sugar beet pectin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The transcriptional activator GaaR of Aspergillus niger is required for release and utilization of d-galacturonic acid from pectin.FEBS Lett. 2016 Jun;590(12):1804-15. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12211. Epub 2016 May 30. FEBS Lett. 2016. PMID: 27174630 Free PMC article.
-
Aspergillus niger RhaR, a regulator involved in L-rhamnose release and catabolism.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014 Jun;98(12):5531-40. doi: 10.1007/s00253-014-5607-9. Epub 2014 Feb 28. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24682478
-
Identification of a Novel L-rhamnose Uptake Transporter in the Filamentous Fungus Aspergillus niger.PLoS Genet. 2016 Dec 16;12(12):e1006468. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006468. eCollection 2016 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27984587 Free PMC article.
-
Pectin structure and biosynthesis.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2008 Jun;11(3):266-77. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2008.03.006. Epub 2008 May 15. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2008. PMID: 18486536 Review.
-
D-galacturonic acid catabolism in microorganisms and its biotechnological relevance.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2009 Mar;82(4):597-604. doi: 10.1007/s00253-009-1870-6. Epub 2009 Jan 22. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19159926 Review.
Cited by
-
Blocking utilization of major plant biomass polysaccharides leads Aspergillus niger towards utilization of minor components.Microb Biotechnol. 2021 Jul;14(4):1683-1698. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.13835. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Microb Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34114741 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning prediction of novel pectinolytic enzymes in Aspergillus niger through integrating heterogeneous (post-) genomics data.Microb Genom. 2021 Dec;7(12):000674. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000674. Microb Genom. 2021. PMID: 34874247 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of Genes Encoding Plant Cell Wall-Degrading Carbohydrate-Active Enzymes by Lignocellulose-Derived Monosaccharides and Cellobiose in the White-Rot Fungus Dichomitus squalens.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 May 17;84(11):e00403-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00403-18. Print 2018 Jun 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29572208 Free PMC article.
-
Space exposure enhanced pectin-degrading enzymes expression and activity in Aspergillus costaricaensis.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Sep 2;39(11):295. doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03740-y. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37658165
-
Vanillic acid and methoxyhydroquinone production from guaiacyl units and related aromatic compounds using Aspergillus niger cell factories.Microb Cell Fact. 2021 Aug 3;20(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s12934-021-01643-x. Microb Cell Fact. 2021. PMID: 34344380 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Voragen AGJ, Coenen GJ, Verhoef RP, Schols HA. Pectin, a versatile polysaccharide present in plant cell walls. Struct. Chem. 2009;20:263–275. doi: 10.1007/s11224-009-9442-z. - DOI
-
- Brett, C. T. & Waldron, K. W. Chapter 2. The molecular component of the wall. In: Physiology and biochemistry of plant cell walls. 4–44 (1996).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

