Hydrogen Inhalation Protects against Ototoxicity Induced by Intravenous Cisplatin in the Guinea Pig
- PMID: 28955207
- PMCID: PMC5601388
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00280
Hydrogen Inhalation Protects against Ototoxicity Induced by Intravenous Cisplatin in the Guinea Pig
Abstract
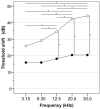
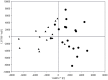
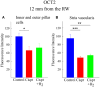
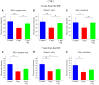
Introduction: Permanent hearing loss and tinnitus as side-effects from treatment with the anticancer drug cisplatin is a clinical problem. Ototoxicity may be reduced by co-administration of an otoprotective agent, but the results in humans have so far been modest. Aim: The present preclinical in vivo study aimed to explore the protective efficacy of hydrogen (H2) inhalation on ototoxicity induced by intravenous cisplatin. Materials and Methods: Albino guinea pigs were divided into four groups. The Cispt (n = 11) and Cispt+H2 (n = 11) groups were given intravenous cisplatin (8 mg/kg b.w., injection rate 0.2 ml/min). Immediately after, the Cispt+H2 group also received gaseous H2 (2% in air, 60 min). The H2 group (n = 5) received only H2 and the Control group (n = 7) received neither cisplatin nor H2. Ototoxicity was assessed by measuring frequency specific ABR thresholds before and 96 h after treatment, loss of inner (IHCs) and outer (OHCs) hair cells, and by performing densitometry-based immunohistochemistry analysis of cochlear synaptophysin, organic transporter 2 (OCT2), and copper transporter 1 (CTR1) at 12 and 7 mm from the round window. By utilizing metabolomics analysis of perilymph the change of metabolites in the perilymph was assessed. Results: Cisplatin induced electrophysiological threshold shifts, hair cell loss, and reduced synaptophysin immunoreactivity in the synapse area around the IHCs and OHCs. H2 inhalation mitigated all these effects. Cisplatin also reduced the OCT2 intensity in the inner and outer pillar cells and in the stria vascularis as well as the CTR1 intensity in the synapse area around the IHCs, the Deiters' cells, and the stria vascularis. H2 prevented the majority of these effects. Conclusion: H2 inhalation can reduce cisplatin-induced ototoxicity on functional, cellular, and subcellular levels. It is proposed that synaptopathy may serve as a marker for cisplatin ototoxicity. The effect of H2 on the antineoplastic activity of cisplatin needs to be further explored.
Keywords: ABR; copper transporter 1; in vivo; inner hair cells; organic cation transporter 2; outer hair cells; perilymph metabolomics; synaptophysin.
Figures






Similar articles
-
MATE1 expression in the cochlea and its potential involvement in cisplatin cellular uptake and ototoxicity.Acta Otolaryngol. 2023 Mar;143(3):242-249. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2023.2184864. Epub 2023 Mar 21. Acta Otolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 36943799
-
Role of the copper transporter, CTR1, in platinum-induced ototoxicity.J Neurosci. 2010 Jul 14;30(28):9500-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1544-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20631178 Free PMC article.
-
Inhalation of Molecular Hydrogen, a Rescue Treatment for Noise-Induced Hearing Loss.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Jun 1;15:658662. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.658662. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34140880 Free PMC article.
-
Supporting Cells and Their Potential Roles in Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity.Front Neurosci. 2022 Apr 27;16:867034. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.867034. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35573297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Membrane transporters as mediators of cisplatin side-effects.Anticancer Res. 2014 Jan;34(1):547-50. Anticancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24403515 Review.
Cited by
-
Current Strategies to Combat Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jul 3;11:999. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00999. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32719605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Middle Ear Administration of a Particulate Chitosan Gel in an in vivo Model of Cisplatin Ototoxicity.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Jun 25;13:268. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00268. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31293387 Free PMC article.
-
Aminoglycoside- and Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity: Mechanisms and Otoprotective Strategies.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2019 Nov 1;9(11):a033548. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a033548. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2019. PMID: 30559254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of MgH2 in Mitigating Cisplatin-Induced Hearing Loss.Neurosci Bull. 2025 Aug 11. doi: 10.1007/s12264-025-01477-2. Online ahead of print. Neurosci Bull. 2025. PMID: 40790374
-
Cisplatin ototoxicity mechanism and antagonistic intervention strategy: a scope review.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Jun 1;17:1197051. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1197051. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37323582 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berglin C. E., Pierre P. V., Bramer T., Edsman K., Ehrsson H., Eksborg S., et al. . (2011). Prevention of cisplatin-induced hearing loss by administration of a thiosulfate-containing gel to the middle ear in a guinea pig model. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 68, 1547–1556. 10.1007/s00280-011-1656-2 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

