Improvement of Bone Physiology and Life Quality Due to Association of Risedronate and Anastrozole
- PMID: 28955236
- PMCID: PMC5601069
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00632
Improvement of Bone Physiology and Life Quality Due to Association of Risedronate and Anastrozole
Abstract
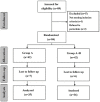
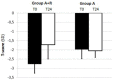
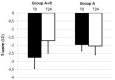
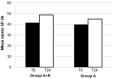
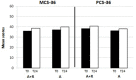
The endocrine therapy is the new frontiers of many breast cancers hormone sensitive. Hormone therapy for treating women with hormone receptor-positive cancer suppresses breast cancer growth either by reducing estrogen synthesis or by interfering with the action of estrogen within tumor cells. In this prospective randomized observational study we investigate the effect of adjuvant anastrozole in monotherapy or associated with risedronate on bone physiology and quality of life in postmenopausal, hormone-sensitive early breast cancer women at mild to moderate risk of fragility fractures. Methods : 84 women were randomly assigned to receive anastrozole alone (group A) or anastrozole plus oral risedronate (group A+R). At baseline and after 24 months lumbar spine (LS) and femoral neck (FN) BMD were evaluated with dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) was examined using the short-form healthy survey. Results : After 24 months, the group A+R has showed a significant increase in T-score for LS (p < 0.05) and for FN (p < 0.05) whereas women of group A had a statistically significant rate of bone loss both in LS T-score (p < 0.05) and in FN (p < 0.05). A significant change in T-score BMD was seen for group A+R compared with group A at the LS (p = 0.04) and at FN (p = 0.04). Finally, group A+R showed an overall significant improvement of health profile (SF-36) in group A (p = 0.03). Conclusion : Postmenopausal breast cancer women with osteopenia during treatment with anastrozole have considerable risk of developing osteoporosis during the first 2 years; preventive measures such as healthy lifestyle and daily supplements of calcium and vitamin D alone seem to be insufficient in holding their bones healthy. Our findings suggest the usefulness of addition of risedronate in order to prevent aromatase inhibitors-related bone loss, not only in case of high-risk of fractures, but also for women at mild-moderate risk. This determines a significant improvement in bone health and a positive impact on HRQoL.
Keywords: anastrozole; bone density; breast cancer; health-related quality of life; risedronate.
Figures
References
-
- Boissier S., Ferreras M., Peyruchaud O., Magnetto S., Ebetino F. H., Colombel M., et al. . (2000). Bisphosphonates inhibit breast and prostate carcinoma cell invasion, an early event in the formation of bone metastases. Cancer Res. 60, 2949–2954. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

