Food and Sex-Related Impacts on the Pharmacokinetics of a Single-Dose of Ginsenoside Compound K in Healthy Subjects
- PMID: 28955238
- PMCID: PMC5602130
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00636
Food and Sex-Related Impacts on the Pharmacokinetics of a Single-Dose of Ginsenoside Compound K in Healthy Subjects
Abstract
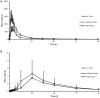
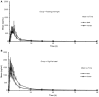
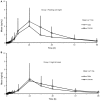
Background and Objectives: Ginsenoside compound K (CK) is a candidate drug for rheumatoid arthritis therapy. This clinical trial was designed to evaluate the effects of food and sex on the pharmacokinetics of CK and its metabolite 20(S)-protopanaxadiol (PPD). Methods: An open-label, single-center, two-period crossover trial was performed in healthy Chinese subjects (n = 24; male = 12, female = 12), randomized to either the fasting overnight or the high-fat meal group before a single 200 mg dose of monomer CK was administered. According to the concentration-time data of plasma and urine samples from each subject, the pharmacokinetic parameters of CK and 20(S)-PPD were calculated and statistically analyzed. Results: A two-way ANOVA test combined with mean plots showed no statistically significant interaction between food and sex. High-fat meal accelerated the absorption of CK, with tmax being shortened from 3.6 to 2.5 h (p = 0.015). In contrast, food significantly increased the Cmax, AUClast, and AUCinf(p < 0.001) with the 90% confidence intervals falling outside of the conventional 0.80-1.25. Females had higher exposure levels of CK than males, but the difference was statistically significant only after a high-fat meal. Of note, CK was rarely excreted in urine. Furthermore, the effects of food and sex were also observed on 20(S)-PPD. Conclusion: High-fat food and sex both had an impact on the disposition of CK in vivo, but rather than a significant interaction effect. High-fat food accelerated and increased the absorption of CK, while the exposure of CK was higher in females compared to males. The results indicate that food and sex should be two noteworthy factors in future research on CK.
Keywords: ChiCTR-IPR-15005787; clinical trial; food effect; ginsenosides compound K; http://www.chictr.org.cn/index.aspx; pharmacokinetics; sex effect.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A narrative review of the pharmacology of ginsenoside compound K.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Feb;10(4):234. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-501. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35280413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single- and Multiple-Dose Trials to Determine the Pharmacokinetics, Safety, Tolerability, and Sex Effect of Oral Ginsenoside Compound K in Healthy Chinese Volunteers.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Jan 11;8:965. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00965. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29375375 Free PMC article.
-
LC-MS/MS determination of ginsenoside compound K and its metabolite 20 (S)-protopanaxadiol in human plasma and urine: applications in a clinical study.Bioanalysis. 2019 Mar;11(5):365-380. doi: 10.4155/bio-2018-0185. Epub 2019 Mar 15. Bioanalysis. 2019. PMID: 30873858
-
Impact of NR1I2, adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette transporters genetic polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics of ginsenoside compound K in healthy Chinese volunteers.J Ginseng Res. 2019 Jul;43(3):460-474. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2018.04.003. Epub 2018 Apr 28. J Ginseng Res. 2019. PMID: 31308818 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetic Comparison of Ginsenosides between Fermented and Non-Fermented Red Ginseng in Healthy Volunteers.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Dec 15;14(12):2807. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122807. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36559300 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of gut microbiota on the pharmacokinetics of protopanaxadiol ginsenosides Rd, Rg3, F2, and compound K in healthy volunteers treated orally with red ginseng.J Ginseng Res. 2020 Jul;44(4):611-618. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2019.05.012. Epub 2019 Jun 5. J Ginseng Res. 2020. PMID: 32617041 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo pharmacokinetics of ginsenoside compound K mediated by gut microbiota.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 23;19(8):e0307286. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307286. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39178246 Free PMC article.
-
Methods on improvements of the poor oral bioavailability of ginsenosides: Pre-processing, structural modification, drug combination, and micro- or nano- delivery system.J Ginseng Res. 2023 Nov;47(6):694-705. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2023.07.005. Epub 2023 Jul 26. J Ginseng Res. 2023. PMID: 38107396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A narrative review of the pharmacology of ginsenoside compound K.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Feb;10(4):234. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-501. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35280413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Triterpenes as Potential Drug Candidates for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment.Life (Basel). 2023 Jul 5;13(7):1514. doi: 10.3390/life13071514. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37511889 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bren L. (2005). Does sex make a difference? FDA Consum. 39, 10–15. Available online at: https://permanent.access.gpo.gov/lps1609/www.fda.gov/fdac/features/2005/... - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

