Nanotechnology: An Untapped Resource for Food Packaging
- PMID: 28955314
- PMCID: PMC5601076
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01735
Nanotechnology: An Untapped Resource for Food Packaging
Abstract
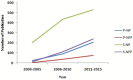
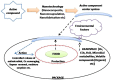
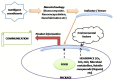
Food commodities are packaged and hygienically transported to protect and preserve them from any un-acceptable alteration in quality, before reaching the end-consumer. Food packaging continues to evolve along-with the innovations in material science and technology, as well as in light of consumer's demand. Presently, the modern consumers of competitive economies demands for food with natural quality, assured safety, minimal processing, extended shelf-life and ready-to-eat concept. Innovative packaging systems, not only ascertains transit preservation and effective distribution, but also facilitates communication at the consumer levels. The technological advances in the domain of food packaging in twenty-first century are mainly chaired by nanotechnology, the science of nano-materials. Nanotechnology manipulates and creates nanometer scale materials, of commercial and scientific relevance. Introduction of nanotechnology in food packaging sector has significantly addressed the food quality, safety and stability concerns. Besides, nanotechnology based packaging intimate's consumers about the real time quality of food product. Additionally, nanotechnology has been explored for controlled release of preservatives/antimicrobials, extending the product shelf life within the package. The promising reports for nanotechnology interventions in food packaging have established this as an independent priority research area. Nanoparticles based food packages offer improved barrier and mechanical properties, along with food preservation and have gained welcoming response from market and end users. In contrary, recent advances and up-liftment in this area have raised various ethical, environmental and safety concerns. Policies and regulation regarding nanoparticles incorporation in food packaging are being reviewed. This review presents the existing knowledge, recent advances, concerns and future applications of nanotechnology in food packaging sector.
Keywords: antimicrobial; nanoparticles; nanosensors; nanotechnology; packaging.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Active food packaging evolution: transformation from micro- to nanotechnology.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2010 Oct;50(9):799-821. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2010.503694. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2010. PMID: 20924864 Review.
-
Recent advances in the application of nanotechnology to create antioxidant active food packaging materials.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024;64(10):2890-2905. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2128035. Epub 2022 Sep 30. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 36178259 Review.
-
Advantages of nanotechnology developments in active food packaging.Food Res Int. 2022 Apr;154:111023. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111023. Epub 2022 Feb 17. Food Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35337578 Review.
-
(Bio)nanotechnology in Food Science-Food Packaging.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Jan 22;11(2):292. doi: 10.3390/nano11020292. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33499415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnology application in food packaging: A plethora of opportunities versus pending risks assessment and public concerns.Food Res Int. 2020 Nov;137:109664. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109664. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Food Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33233243 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis, Characterization, and Docking Study of Novel Thioureidophosphonate-Incorporated Silver Nanocomposites as Potent Antibacterial Agents.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jun 6;15(6):1666. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15061666. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37376114 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Nanomaterials for Food Packaging.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 May 29;11(6):729. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11060729. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35740136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A proteome-wide assessment of the oxidative stress paradigm for metal and metal-oxide nanomaterials in human macrophages.NanoImpact. 2020 Jan;17:10.1016/j.impact.2019.100194. doi: 10.1016/j.impact.2019.100194. Epub 2019 Nov 23. NanoImpact. 2020. PMID: 32133426 Free PMC article.
-
Metal-based nanoparticles, sensors, and their multifaceted application in food packaging.J Nanobiotechnology. 2021 Aug 26;19(1):256. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-00996-0. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021. PMID: 34446005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanocomposites and their application in antimicrobial packaging.Front Chem. 2024 Feb 26;12:1356304. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1356304. eCollection 2024. Front Chem. 2024. PMID: 38469428 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adame D., Beall G. W. (2009). Direct measurement of the constrained polymer region in polyamide/clay nanocomposites and the implications for gas diffusion. Appl. Clay Sci. 42, 545–552. 10.1016/j.clay.2008.03.005 - DOI
-
- Advantage Magazine (2004). Nanotechnology and Food Packaging. Available inline at: http://www.azonano.com/Details.asp?ArticleID=857
-
- An J., Zhang M., Wang S., Tang J. (2008). Physical, chemical and microbiological changes in stored green asparagus spears as affected by coating of silver nanoparticles-PVP. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 41, 1100–1107. 10.1016/j.lwt.2007.06.019 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

