Bacterial Wilt in China: History, Current Status, and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 28955350
- PMCID: PMC5601990
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01549
Bacterial Wilt in China: History, Current Status, and Future Perspectives
Abstract
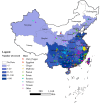
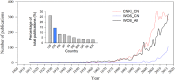
Bacterial wilt caused by plant pathogenic Ralstonia spp. is one of the most important diseases affecting the production of many important crops worldwide. In China, a large scientific community has been dedicated to studying bacterial wilt and its causative agent, Ralstonia pseudosolanacearum and R. solanacearum. Most of their work was published in Chinese, which has hindered international communication and collaboration in this field. In this review, we summarize the status of knowledge on geographical distribution, diversity, and host range of Ralstonia spp., as well as, the impact of bacterial wilt on important crops and disease control approaches, in China. We present areas of research and publications by Chinese scientists and propose the promotion of collaborative research within China and with the international community.
Keywords: China; bacterial wilt; distribution; diversity; host range.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Different Sequevars of Ralstonia pseudosolanacearum Causing Bacterial Wilt of Bidens pilosa in China.Plant Dis. 2020 Nov;104(11):2768-2773. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-12-19-2738-SC. Epub 2020 Sep 11. Plant Dis. 2020. PMID: 32915706
-
Antagonistic Activity of Volatile Organic Compounds Produced by Acid-Tolerant Pseudomonas protegens CLP-6 as Biological Fumigants To Control Tobacco Bacterial Wilt Caused by Ralstonia solanacearum.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Feb 28;89(2):e0189222. doi: 10.1128/aem.01892-22. Epub 2023 Feb 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36722969 Free PMC article.
-
Biocontrol of the Major Plant Pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum in Irrigation Water and Host Plants by Novel Waterborne Lytic Bacteriophages.Front Microbiol. 2019 Dec 6;10:2813. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02813. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31866979 Free PMC article.
-
Ralstonia solanacearum, a widespread bacterial plant pathogen in the post-genomic era.Mol Plant Pathol. 2013 Sep;14(7):651-62. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12038. Epub 2013 May 30. Mol Plant Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23718203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacteriophage-Based Bacterial Wilt Biocontrol for an Environmentally Sustainable Agriculture.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Jul 14;8:1218. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01218. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28769942 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring rhizo-microbiome transplants as a tool for protective plant-microbiome manipulation.ISME Commun. 2022 Feb 1;2(1):10. doi: 10.1038/s43705-022-00094-8. ISME Commun. 2022. PMID: 37938685 Free PMC article.
-
Biocontrol of Tomato Bacterial Wilt by Foliar Spray Application of a Novel Strain of Endophytic Bacillus sp.Microbes Environ. 2020;35(4):ME20078. doi: 10.1264/jsme2.ME20078. Microbes Environ. 2020. PMID: 33012743 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomics and host range analysis of four Ralstonia pseudosolanacearum strains isolated from sunflower reveals genomic and phenotypic differences.BMC Genomics. 2024 Feb 19;25(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10087-7. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38373891 Free PMC article.
-
WIPK-NtLTP4 pathway confers resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum in tobacco.Plant Cell Rep. 2022 Jan;41(1):249-261. doi: 10.1007/s00299-021-02808-z. Epub 2021 Oct 25. Plant Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 34697685
-
Pre-soil fumigation with ammonium bicarbonate and lime modulates the rhizosphere microbiome to mitigate clubroot disease in Chinese cabbage.Front Microbiol. 2024 Apr 15;15:1376579. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1376579. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38686113 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cai Y., Liao Z., Zhang J., Kong W., He C. (2003). Effect of ecological organic fertilizer on tomato bacterial wilt and soil microbial diversities. J. Appl. Ecol. 14 349–353. - PubMed
-
- Cao J. (1982). Investigation report of bacterial wilt in Eucalyptus saligna and E. grandis. Guangxi For. Sci. 4 30–31.
-
- Chai X., Dai H. (1994). Occurrence and control of Mulberry bacterial wilt in Zhejiang Province. Bull. Seric. 25 53.
-
- Champoiseau P. G., Jones J. B., Allen C. (2009). Ralstonia solanacearum Race 3 biovar 2 causes tropical losses and temperate anxieties. Plant Health Prog. 10 10.1094/PHP-2009-0313-01-RV - DOI
-
- Chen B., Jiang H., Liao B., Ren X. (2007). Progress on groundnut genetic enhancement for bacterial wilt resistance. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 23 369–372. 10.1094/PHP-2009-0313-01-RV - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

