Phosphorous Application Improves Drought Tolerance of Phoebe zhennan
- PMID: 28955356
- PMCID: PMC5601402
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01561
Phosphorous Application Improves Drought Tolerance of Phoebe zhennan
Abstract
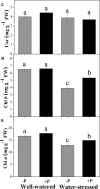
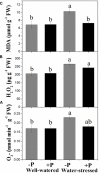
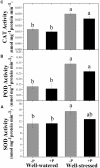
Phoebe zhennan (Gold Phoebe) is a threatened tree species in China and a valuable and important source of wood and bioactive compounds used in medicine. Apart from anthropogenic disturbances, several biotic constraints currently restrict its growth and development. However, little attention has been given to building adaptive strategies for its conservation by examining its morphological and physio-biochemical responses to drought stress, and the role of fertilizers on these responses. A randomized experimental design was used to investigate the effects of two levels of irrigation (well-watered and drought-stressed) and phosphorous (P) fertilization treatment (with and without P) to assess the morphological and physio-biochemical responses of P. zhennan seedlings to drought stress. In addition, we evaluated whether P application could mitigate the negative impacts of drought on plant growth and metabolism. Drought stress had a significant negative effect on the growth and metabolic processes of P. zhennan. Despite this, reduced leaf area, limited stomatal conductance, reduced transpiration rate, increased water use efficiency, enhanced antioxidant enzymes activities, and osmolytes accumulation suggested that the species has good adaptive strategies for tolerating drought stress. Application of P had a significant positive effect on root biomass, signifying its improved water extracting capacity from the soil. Moreover, P fertilization significantly increased leaf relative water content, net photosynthetic rate, and maximal quantum efficiency of PSII under drought stress conditions. This may be attributable to several factors, such as enhanced root biomass, decreased malondialdehyde content, and the up-regulation of chloroplast pigments, osmolytes, and nitrogenous compounds. However, P application had only a slight or negligible effect on the growth and metabolism of well-watered plants. In conclusion, P. zhennan has a strong capability for drought resistance, while P application facilitates and improves drought tolerance mostly through physio-biochemical adjustments, regardless of water availability. It is imperative to explore the underlying metabolic mechanisms and effects of different levels of P fertilization on P. zhennan under drought conditions in order to design appropriate conservation and management strategies for this species, which is at risk of extinction.
Keywords: Phoebe zhennan; conservation; drought stress; drought tolerance; phosphorous fertilization.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phosphorous fertilization alleviates drought effects on Alnus cremastogyne by regulating its antioxidant and osmotic potential.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 4;8(1):5644. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24038-2. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29618772 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of phosphorus application on drought resistant responses of Eucalyptus grandis seedlings.Physiol Plant. 2019 Aug;166(4):894-908. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12868. Epub 2019 Jan 9. Physiol Plant. 2019. PMID: 30414178
-
Effects of Elevated Ozone Levels on Photosynthesis, Biomass and Non-structural Carbohydrates of Phoebe bournei and Phoebe zhennan in Subtropical China.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Nov 30;9:1764. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01764. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 30555502 Free PMC article.
-
Drought Stress Impacts on Plants and Different Approaches to Alleviate Its Adverse Effects.Plants (Basel). 2021 Jan 28;10(2):259. doi: 10.3390/plants10020259. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33525688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticle-mediated amelioration of drought stress in plants: a systematic review.3 Biotech. 2023 Oct;13(10):336. doi: 10.1007/s13205-023-03751-4. Epub 2023 Sep 8. 3 Biotech. 2023. PMID: 37693636 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pre treatment with Bacillus subtilis mitigates drought induced photo-oxidative damages in okra by modulating antioxidant system and photochemical activity.Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2021 May;27(5):945-957. doi: 10.1007/s12298-021-00982-8. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2021. PMID: 34092946 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses uncover the drought adaption landscape of Phoebe zhennan.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Mar 3;22(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03474-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 35240986 Free PMC article.
-
Piriformospora indica confers salinity tolerance on tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) through amelioration of nutrient accumulation, K+/Na+ homeostasis and water status.Plant Cell Rep. 2019 Sep;38(9):1151-1163. doi: 10.1007/s00299-019-02434-w. Epub 2019 May 31. Plant Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31152194
-
Molecular and Hormonal Aspects of Drought-Triggered Flower Shedding in Yellow Lupine.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 31;20(15):3731. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153731. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31370140 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorus Fertilization and Chemical Root Pruning: Effects on Root Traits During the Nursery Stage in Two Mediterranean Species from Central Chile.Plants (Basel). 2025 Jan 12;14(2):195. doi: 10.3390/plants14020195. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39861548 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Karaki G. N., Clark R. B., Sullivan C. Y. (1996). Phosphorous nutrition and water stress effects on proline accumulation in sorghum and bean. J. Plant Physiol. 148 745–751. 10.1016/S0176-1617(96)80378-6 - DOI
-
- Anjum S. A., Xie X., Wang L., Saleem M. F., Man C., Lei W. (2011). Morphological, physiological and biochemical responses of plants to drought stress. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 6 2026–2032.
-
- Azcon R., Gomez M., Tobar R. (1996). Physiological and nutritional responses by Lactuca sativa L. to nitrogen sources and mychorrhizal fungi under drought condition. Biol. Fertil. Soils 22 156–161. 10.1007/BF00384448 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

