Combined Effects of Elevated O3 Concentrations and Enhanced UV-B Radiation of the Biometric and Biochemical Properties of Soybean Roots
- PMID: 28955360
- PMCID: PMC5600998
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01568
Combined Effects of Elevated O3 Concentrations and Enhanced UV-B Radiation of the Biometric and Biochemical Properties of Soybean Roots
Abstract
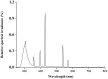
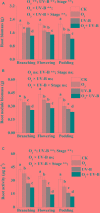
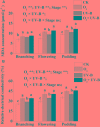
Enhanced ultraviolet-B (UV-B) radiation and elevated tropospheric ozone alone may inhibit the growth of agricultural crops. However, research regarding their combined effects on growth and biochemical properties of roots is still scarce. Using open top chambers, we monitored the response of growth, secondary metabolites, endogenous hormones and enzyme activities of soybean roots to elevated O3 and enhanced UV-B individually and in combination at stages of branching, flowering and podding. Our results indicated that the root biomass decreased by 23.6, 25.2, and 27.7%, and root oxidative capacity declined by11.2, 39.9, and 55.7% exposed to elevated O3, enhanced UV-B, and O3 + UV-B, respectively, compared to the control treatment. Concentrations of quercetin and ABA were significantly increased, while concentrations of total polyphenol and P-coumaric acid responded insignificantly to elevated O3, enhanced UV-B, and O3 + UV-B during the whole period of soybean growth. Elevated O3, enhanced UV-B and O3 + UV-B showed significant negative effects on superoxide dismutase (EC 1.15.1.1) activity at flowering stage, on activities of peroxidase (EC 1.11.1.7) and catalase (EC 1.11.1.6) at podding stage, on ascorbate peroxidase activity during the whole period of soybean growth. Moreover, compared to hormones and enzyme activity, secondary metabolisms showed stronger correlation with root growth exposed to elevated O3 and enhanced UV-B individually and in combination. Our study concluded that combined effects of O3 and UV-B radiation significantly exacerbated the decline of soybean root growth, and for annual legumes, the inhibited root growth exposed to O3 and/or UV-B radiation was mostly associated with secondary metabolisms (especially flavonoids).
Keywords: endogenous hormones; enzyme activities; flavonoids; open-top chambers; soybean roots.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Combined effects of O3 and UV radiation on secondary metabolites and endogenous hormones of soybean leaves.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 14;12(8):e0183147. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183147. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28806739 Free PMC article.
-
Interactive effects of elevated ozone and UV-B radiation on soil nematode diversity.Ecotoxicology. 2014 Jan;23(1):11-20. doi: 10.1007/s10646-013-1146-x. Epub 2013 Oct 25. Ecotoxicology. 2014. PMID: 24158399
-
Response of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus concentration and stoichiometry of plants and soils during a soybean growth season to O3 stress and straw return in Northeast China.Sci Total Environ. 2022 May 20;822:153573. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153573. Epub 2022 Feb 2. Sci Total Environ. 2022. PMID: 35122851
-
Separate and combined responses to water deficit and UV-B radiation.Plant Sci. 2013 Dec;213:98-105. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.09.003. Epub 2013 Sep 7. Plant Sci. 2013. PMID: 24157212 Review.
-
Effect of elevated CO2, O3, and UV radiation on soils.ScientificWorldJournal. 2014 Feb 6;2014:730149. doi: 10.1155/2014/730149. eCollection 2014. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014. PMID: 24688424 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Morphophysiological and Proteomic Responses on Plants of Irradiation with Electromagnetic Waves.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 12;22(22):12239. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212239. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental effects of ozone depletion, UV radiation and interactions with climate change: UNEP Environmental Effects Assessment Panel, update 2017.Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2018 Feb 14;17(2):127-179. doi: 10.1039/c7pp90043k. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29404558 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological responses of Lepidium meyenii plants to ultraviolet-B radiation challenge.BMC Plant Biol. 2019 May 7;19(1):186. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1755-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 31064341 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albacete A., Ghanem M. E., Martinez-Andujar C., Acosta M., Sanchez- Bravo J., Martinez V., et al. (2008). Hormonal changes in relation to biomass partitioning and shoot growth impairment in salinized tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) plants. J. Exp. Bot. 59 4119–4131. 10.1093/jxb/ern251 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ambasht N. K., Agrawal M. (2003). Effects of enhanced UV-B radiation and tropospheric ozone on physiological and biochemical characteristics of field grown wheat. Biol. Plant. 47 625–628. 10.1023/B:BIOP.0000041076.95209.c3 - DOI
-
- Ando T., Yoshida S., Nishiyama I. (1983). Nature of oxidizing power of rice roots. Plant Soil 72 57–71. 10.1007/BF02185094 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

