The cost of cancer treatment in Portugal
- PMID: 28955401
- PMCID: PMC5606294
- DOI: 10.3332/ecancer.2017.765
The cost of cancer treatment in Portugal
Abstract
Introduction: Cancer is the second most common cause of death in Portugal, with 24.3% of these deaths caused by malignant neoplasms. The strong impact on lost productivity and rising treatment costs make cancer a priority. In order to understand, compare, and control costs by promoting transparency in the health system, it is vital to analyse the cost of oncological diseases. This study aims to estimate the economic burden associated with the treatment of cancer in Portugal by calculating the direct medical costs.
Materials and methods: A prevalence-based study was conducted. The approaches used to estimate the costs were the top-down and gross costing techniques. In order to identify, quantify, and value all of the costs associated with the treatment of cancer, several sources of data were consulted to obtain the most up-to-date information on hospital care and a modified Delphi Panel was created to obtain data on primary health care.
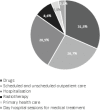
Results: The annual cost of cancer treatment in Portugal amounted to 867 million euros, representing 5.5% of the total expenditure for health and 84 euros per capita. The main component of this cost is antineoplastic drugs, which account for 31.5% of the total.
Discussion and conclusion: By comparing the costs calculated in this study with those of the single Portuguese study conducted in 2009 and the European study carried out in 2013, we found that the annual cost for cancer treatment increased by about 300 million euros. An increase in incidence and the rising cost of drugs can explain this difference.
Keywords: cancer; costs; economics; health; health technology assessment.
Figures
References
-
- European Cancer Observatory, International Agency for Research on Cancer. Estimated Cancer Incidence, Mortality and Prevalence, 2012, Portugal. [January 17]. Available at: Http://eco.iarc.fr/EUCAN/Country.aspx?ISOCountryCd=620.
-
- National Statistics Institute Statistical Yearbook of Portugal. Lisbon: INE; 2014. 2014.
-
- ORGANIZATION FOR ECONOMIC CO-OPERATION AND DEVELOPMENT - OECD. OECD.Stat. [December 16]. Available at: Http://stats.oecd.org/viewhtml.aspx?datasetcode=HEALTH_STAT&lang=en.
-
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. Portugal: 2015. [March 17]. Global Burden of disease. Available at: Http://ghdx.healthdata.org/gbd-results-tool.
-
- Think Tank. 2nd. Lisbon: National School of Public Health; 2014. Inovar Saúde (Innovate Health) Pensar a Saúde: acesso do cidadão à inovação terapêutica – Oncologia (Think Health: citizen’s access to therapeutic innovation - Oncology)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources