Methotrexate and low-dose prednisolone downregulate osteoclast function by decreasing receptor activator of nuclear factor-κβ expression in monocytes from patients with early rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 28955481
- PMCID: PMC5604603
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2016-000365
Methotrexate and low-dose prednisolone downregulate osteoclast function by decreasing receptor activator of nuclear factor-κβ expression in monocytes from patients with early rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objective: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic, immune-mediated inflammatory disease that ultimately leads to bone erosions and joint destruction. Methotrexate (MTX) slows bone damage but the mechanism by which it acts is still unknown. In this study, we aimed to assess the effect of MTX and low-dose prednisolone (PDN) on circulating osteoclast (OC) precursors and OC differentiation in patients with RA.
Methods: Patients with RA before and at least 6 months after MTX therapy were analysed and compared with healthy donors. A blood sample was collected in order to assess receptor activator of NF-κβ (RANK) ligand surface expression on circulating leucocytes and frequency and phenotype of monocyte subpopulations. Quantification of serum levels of bone turnover markers and cytokines and OC differentiation assays were performed.
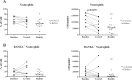
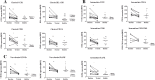
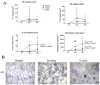
Results: Classical activation markers of monocytes and RANK increased in patients with RA at baseline, compared with control healthy donors, and after MTX and low-dose PDN (MTX+PDN) exposure they decreased to control levels. Although the number of OC was not different between groups, the percentage of resorbed area and the resorbed area per pit reduced after treatment. Serum soluble receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa (RANKL) levels increased at baseline compared with healthy donors and normalised after therapy.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that MTX+PDN play an important role in downregulating OC function, which we believe occurs through the decrease in RANK surface expression in monocytes.
Keywords: Bone; DMARD; Monocytes; Osteoclast; Rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
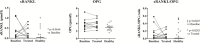
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
