ProNGF-p75NTR axis plays a proinflammatory role in inflamed joints: a novel pathogenic mechanism in chronic arthritis
- PMID: 28955492
- PMCID: PMC5604749
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2017-000441
ProNGF-p75NTR axis plays a proinflammatory role in inflamed joints: a novel pathogenic mechanism in chronic arthritis
Erratum in
-
Correction: ProNGF-p75NTR axis plays a proinflammatory role in inflamed joints: a novel pathogenic mechanism in chronic arthritis.RMD Open. 2018 Jan 7;4(1):e000441corr1. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2017-000441corr1. eCollection 2017. RMD Open. 2018. PMID: 29333280 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: To identify the role of mature nerve growth factor (mNGF), its immature form proNGF and their receptors in arthritis inflammation.
Methods: Real-time PCR, western blot and ELISA were performed to evaluate NGF, proNGF, their receptor and cytokine expression in synovial tissue and cells of patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and controls.
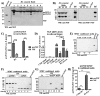
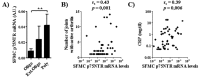
Results: proNGF and not mNGF is the prevalent form measured in synovial fluids of patients with JIA and RA with synovial fibroblasts as a major source of proNGF in the inflamed synoviae. p75NTR, the specific receptor for proNGF, is the NGF receptor most expressed in mononuclear cells of patients with JIA, while TrkA is the prevalent receptor in healthy donors. In ex vivo experiments the effects of proNGF differ from those of mNGF, suggesting that the balance of p75NTR and TrkA expression represents a critical factor in regulating mNGF/proNGF functions, determining which intracellular pathways and biological activities are triggered. Contrary to NGF, proNGF administration increased inflammatory cytokines but not interleukin (IL)-10 expression, inducing a stronger activation of p38 and JNK pathways. proNGF effects depend on its binding to p75NTR, as inhibition of p75NTR with neutralising antibodies or LM11A-31 abolished proNGF-induced production of IL-6 in patients' mononuclear cells, while inhibition of TrkA did not. There is a correlation in patients with arthritis between high p75NTR levels and severity of clinical symptoms.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that an active proNGF-p75NTR axis promotes proinflammatory mechanisms contributing to chronic tissue inflammation, and that the use of p75NTR inhibitors may represent a new therapeutic approach in chronic arthritis.
Keywords: cytokines; inflammation; juvenile idiopathic arthritis; rheumatoid arthritis; synovial fluid.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pro Nerve Growth Factor and Its Receptor p75NTR Activate Inflammatory Responses in Synovial Fibroblasts: A Novel Targetable Mechanism in Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 4;13:818630. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.818630. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35309353 Free PMC article.
-
Nerve growth factor downregulates inflammatory response in human monocytes through TrkA.J Immunol. 2014 Apr 1;192(7):3345-54. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300825. Epub 2014 Feb 28. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24585880
-
ProNGF, but Not NGF, Switches from Neurotrophic to Apoptotic Activity in Response to Reductions in TrkA Receptor Levels.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Mar 9;18(3):599. doi: 10.3390/ijms18030599. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28282920 Free PMC article.
-
NGF and ProNGF: Regulation of neuronal and neoplastic responses through receptor signaling.Adv Biol Regul. 2015 May;58:16-27. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2014.11.003. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Adv Biol Regul. 2015. PMID: 25491371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ProNGF, sortilin, and age-related neurodegeneration.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Nov;1119:208-15. doi: 10.1196/annals.1404.024. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 18056969 Review.
Cited by
-
The Mechanism of Action between Pulsed Radiofrequency and Orthobiologics: Is There a Synergistic Effect?Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 3;23(19):11726. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911726. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nerve Growth Factor and the Role of Inflammation in Tumor Development.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jan 23;46(2):965-989. doi: 10.3390/cimb46020062. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38392180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Topical delivery of nerve growth factor for treatment of ocular and brain disorders.Neural Regen Res. 2021 Sep;16(9):1740-1750. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.306062. Neural Regen Res. 2021. PMID: 33510063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intranasal nerve growth factor for prevention and recovery of the outcomes of traumatic brain injury.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Apr;18(4):773-778. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.354513. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 36204836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Remodeling the Epigenome Through Meditation: Effects on Brain, Body, and Well-being.Subcell Biochem. 2025;108:231-260. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-75980-2_7. Subcell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39820865 Review.
References
-
- Bracci-Laudiero L. Nerve growth factor and inflammation: a complex bidirectional interaction. BrainImmune. 2010. http://brainimmune.com/nerve-growth-factor-and-inflammation-a-complex-bi....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
