Dental findings in marfan syndrome: a case report
- PMID: 28955598
- PMCID: PMC5573476
- DOI: 10.17096/jiufd.78944
Dental findings in marfan syndrome: a case report
Abstract
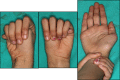
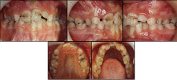
Marfan syndrome is an autosomal dominant disorder of connective tissue primarily characterized with anomalies affecting the musculoskeletal system, the cardiovascular system and the eyes. It has been suggested that early diagnosis of the syndrome is important, because of the risk of infective endocarditis. A 7-year-old female was referred to our clinic, with a chief complaint of dental crowding in the anterior region of mandible. It was observed that the patient needed multiple treatments based on detailed clinical and radiographic examinations. The treatment was carried out with antibiotic prophylaxis an hour prior to her appointment considering her profound caries. The patient was advised to visit regularly for follow up and she was referred for orthodontic evaluation.
Keywords: Marfan syndrome; antibiotic prophylaxis; dental management; infective endocarditis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None declared.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Blunt Injury Forearm Debridement Under Ultrasound-Guided Regional Anesthesia for a Marfan Syndrome Patient.Cureus. 2021 Jan 15;13(1):e12729. doi: 10.7759/cureus.12729. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 33614332 Free PMC article.
-
[Dental aspects of Marfan syndrome].Ned Tijdschr Tandheelkd. 2022 Jan;129(1):17-22. doi: 10.5177/ntvt.2022.01.21098. Ned Tijdschr Tandheelkd. 2022. PMID: 35015388 Dutch.
-
Cardiovascular characteristics in Marfan syndrome and their relation to the genotype.Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2009;71(6):335-71. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2009. PMID: 20232788 Review.
-
Viridans streptococcal (Streptococcus intermedius) mitral valve subacute bacterial endocarditis (SBE) in a patient with mitral valve prolapse after a dental procedure: the importance of antibiotic prophylaxis.Heart Lung. 2010 Jan-Feb;39(1):64-72. doi: 10.1016/j.hrtlng.2009.01.004. Epub 2009 Jul 10. Heart Lung. 2010. PMID: 20109987
-
Marfan syndrome: a review of the literature and case report.Spec Care Dentist. 2013 Sep-Oct;33(5):248-54. doi: 10.1111/scd.12018. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Spec Care Dentist. 2013. PMID: 23980558 Review.
Cited by
-
Periodontal condition in growing subjects with Marfan Syndrome: a case-control study.PeerJ. 2019 Apr 23;7:e6606. doi: 10.7717/peerj.6606. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 31065451 Free PMC article.
-
Blunt Injury Forearm Debridement Under Ultrasound-Guided Regional Anesthesia for a Marfan Syndrome Patient.Cureus. 2021 Jan 15;13(1):e12729. doi: 10.7759/cureus.12729. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 33614332 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shirley ED, Sponseller PD. Marfan syndrome. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2009;17(9):572–581. - PubMed
-
- Rybczynski M, Bernhardt AM, Rehder U, Fuisting B, Meiss L, Voss U, Habermann C, Detter C, Robinson PN, Arslan-Kirchner M, Schmidtke J, Mir TS, Berger J, Meinertz T, von Kodolitsch Y. The spectrum of syndromes and manifestations in individuals screened for suspected Marfan syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2008;146A(24):3157–3166. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.32595. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
