Acute Compartment Syndrome Which Causes Rhabdomyolysis by Carbon Monoxide Poisoning and Sciatic Nerve Injury Associated with It: A Case Report
- PMID: 28955688
- PMCID: PMC5612982
- DOI: 10.5371/hp.2017.29.3.204
Acute Compartment Syndrome Which Causes Rhabdomyolysis by Carbon Monoxide Poisoning and Sciatic Nerve Injury Associated with It: A Case Report
Abstract
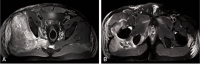
Rhabdomyolysis is most frequently caused by soft tissue injury with trauma to the extremities. Non-traumatic rhabdomyolysis may be caused by alcohol or drug abuse, infection, collagen disease, or intensive exercise, but incidence is low. In particular, rhabdomyolysis resulting from carbon monoxide poisoning is especially rare. If caught before death, carbon monoxide poisoning has been shown to cause severe muscle necrosis and severe muscle damage leading to acute renal failure. In cases of carbon-monoxide-induced rhabdomyolsis leading to acute compartment syndrome in the buttocks and sciatic nerve injury are rare. We have experience treating patients with acute compartment syndrome due to rhabdomyolysis following carbon monoxide poisoning. We report the characteristic features of muscle necrosis observed during a decompression operation and magnetic resonance imaging findings with a one-year follow-up in addition to a review of the literature.
Keywords: Carbon monoxide poisoning; Gluteal compartment syndrome; Magnetic resonance imaging; Rhabdomyolysis; Sciatic neuropathy.
Figures



References
-
- Lee HY, Lee KH, Han JS, Ahn CR, Kim SG, Lee JS. The Tc-MDP bone scan in the cases of acute renal failure due to carbon monoxide poisoning. Korean J Nephrol. 1985;4:56–67.
-
- Chung KJ, Chung YK, Yoo JH, Wang JS. Sciatic nerve palsy complicating gluteal compartment syndrome due to rhabdomyolysis: a case report. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2005;40:103–106.
-
- Thomas MA, Ibels LS. Rhabdomyolysis and acute renal failure. Aust N Z J Med. 1985;15:623–628. - PubMed
-
- Kim HY, Choi SO, Shin SJ, et al. Analysis of 250 cases of rhabdomyolysis. Korean J Nephrol. 1994;13:810–817.
-
- Kang SW, Kim YW, Kim YH. Analysis of nontraumatic rhabdo myolysis during recent 2 years. Korean J Med. 2004;67:467–474.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

