Biosensors based on electrochemical lactate detection: A comprehensive review
- PMID: 28955805
- PMCID: PMC5600356
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2015.11.010
Biosensors based on electrochemical lactate detection: A comprehensive review
Abstract
Lactate detection plays a significant role in healthcare, food industries and is specially necessitated in conditions like hemorrhage, respiratory failure, hepatic disease, sepsis and tissue hypoxia. Conventional methods for lactate determination are not accurate and fast so this accelerated the need of sensitive biosensors for high-throughput screening of lactate in different samples. This review focuses on applications and developments of various electrochemical biosensors based on lactate detection as lactate being essential metabolite in anaerobic metabolic pathway. A comparative study to summarize the L-lactate biosensors on the basis of different analytical properties in terms of fabrication, sensitivity, detection limit, linearity, response time and storage stability has been done. It also addresses the merits and demerits of current enzyme based lactate biosensors. Lactate biosensors are of two main types - lactate oxidase (LOD) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) based. Different supports tried for manufacturing lactate biosensors include membranes, polymeric matrices-conducting or non-conducting, transparent gel matrix, hydrogel supports, screen printed electrodes and nanoparticles. All the examples in these support categories have been aptly discussed. Finally this review encompasses the conclusion and future emerging prospects of lactate sensors.
Keywords: Biosensor; Lactate; Lactate dehydrogenase; Lactate oxidase; Nanomaterials.
Figures
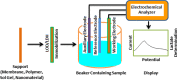





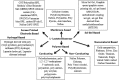
References
-
- Kost G.J. New whole blood analyzers and their impact on cardiac and critical care. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1993;30:153–202. - PubMed
-
- Bakker J., Gris P., Coffernils M., Kahn R.J., Vincent J.L. Serial blood lactate levels can predict the development of multiple organ failure following septic shock. Am. J. Surg. 1996;171:221–226. - PubMed
-
- Parra A., Casero E., Vazquez L., Pariente F., Lorenzo E. Design and characterization of a lactate biosensor based on immobilized lactate oxidase onto gold surfaces. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2006;555:308–315.
-
- Wang J. Amperometric biosensors for clinical and therapeutic drug monitoring: a review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1999;19:47–53. - PubMed
-
- Pilloton R., Nwosu T.N., Mascini M. Amperometric determination of lactic acid. Applications on milk samples. Anal. Lett. 1988;21:727–740.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

