Detection of microwave radiation of cytochrome CYP102 A1 solution during the enzyme reaction
- PMID: 28955835
- PMCID: PMC5600332
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2015.12.013
Detection of microwave radiation of cytochrome CYP102 A1 solution during the enzyme reaction
Abstract
Microwave radiation at 3.4-4.2 GHz frequency of the cytochrome P450 CYP102 A1 (BM3) solution was registered during the lauric acid hydroxylation reaction. The microwave radiation generation was shown to occur following the addition of electron donor NADPH to a system containing an enzyme and a substrate. The radiation occurs for the enzyme solutions with enzyme concentrations of 10-8 and 10-9 М. The microwave radiation effect elicited by the aqueous enzyme solution was observed for the first time. The results obtained can be used to elaborate a new approach to enzyme systems research, including studying of the mechanism of interaction of a functioning enzyme system with microenvironment.
Keywords: Cytochrome P450; Microwave radiation; Monooxygenase system.
Figures
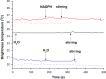
- –
Temperature of measurements 18 °С (dotted lines) and 23 °С (solid lines);
- –
(blue lines) the solution under analysis contains protein CYP102 A1 (10−9 M) and substrate (lauric acid, 0.5 mM) (variant 1);
- –
(red lines) the solution under analysis contains substrate (lauric acid 0.5 mM) upon addition of electron donor (NADPH, 0.2 mM) (variant 2).
- –
(black line) the solution under analysis contains protein CYP102 A1 (10−9 M) (variant 3);
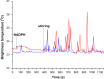
- –
cytochrome CYP102 A1 concentration 10−8 М (blue line) and 10−9 М (red line);
- –
the temperature of solution under analysis is 23 °С;
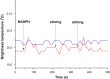
- –
cytochrome CYP102 A1 concentration 10−8 М (blue line) and 10−9 М (red line);
- –
the temperature of solution under analysis is 18 °С;

- –
the temperature of solution under analysis is 23 °С;
- –
(blue line) the solution under analysis contains protein CYP102 A1 (wild type, 10−9 M) and substrate (hexane, 1% v/v);
- –
(red line) the solution under analysis contains protein CYP102 A1 (mutant form, 10−9 M) and substrate (lauric acid, 0.5 mM);
References
-
- Аrchakov A.I., Bachmanova G.I. Taylor&Francis; London, New York, Philadelphia: 1990. Cytochrome P450 and Active Oxygen; p. 275.
-
- Ortiz de Montellano P.R. Plenum Press; New York: 1995. Cytochrome P450: Structure, Mechanism, and Biochemistry.
-
- Miura Y., Fulco A.J. (Omega -2) hydroxylation of fatty acids by a soluble system from Bacillus megaterium. J .Biol. Chem. 1974;249:1880–1888. - PubMed
-
- Narhi L.O., Fulco A.J. Characterization of a catalytically self-sufficient 119,000-dalton cytochrome P-450 monooxygenase induced by barbiturates in Bacillus megaterium. J. Biol. Chem. 1986;261:7160–7169. - PubMed
-
- Miura Y., Fulco A.J. Omega-1, Omega-2 and Omega-3 hydroxylation of long-chain fatty acids, amides and alcohols by a soluble enzyme system from Bacillus megaterium. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1975;388:305–317. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

