Generation and characterization of monoclonal antibody against Advanced Glycation End Products in chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 28955871
- PMCID: PMC5600449
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2016.03.011
Generation and characterization of monoclonal antibody against Advanced Glycation End Products in chronic kidney disease
Abstract
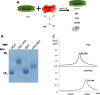
Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs) are toxins that are involved in structural and functional alterations of several organs and tissues, resulting in various pathologies. Several types of AGEs have been described but carboxymethyllysine (CML) is the major antigenic AGE compound. In this study, three different immunogenic carrier proteins (KLH, keyhole limpet hemocyanin; BSA, bovine serum albumin; and HSA, human serum albumin) were modified by glycation. The glycated molecules were used to produce epitope-specific monoclonal antibodies able to recognize the CML domain and to detect uremic toxins in the serum of patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). A competitive ELISA was standardized in order to quantify CML in the sera of CKD patients. An increase in uremic toxins can compromise the clinical condition of these patients, thus, the detection and quantification of these toxins should contribute to a better management and understanding of this disease.
Keywords: Age; CML; Chronic kidney disease; Monoclonal antibody.
Figures



References
-
- El Nahas M. Cardio-kidney-damage: a unifying concept. Kidney Int. 2010;78:14–18. - PubMed
-
- De Lima A.O., Kesrouani S., Gomes R.A. Population screening for chronic kidney disease: a survey involving 38 721 Brazilians. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2012;0:1–4. - PubMed
-
- National Kidney Foundation, K/DOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines for Chronic Kidney Disease: Evaluation, Classification and Stratification. Am. J. Kidney Dis. vol. 39, 2013, pp. S1–S266. 〈https://www.kidney.org/sites/default/files/docs/ckd_evaluation_classific...〉 - PubMed
-
- Vanholder R., De Smet R., Glorieux G., Argilés A. European Uremic Toxin Work Group (EUTox). Review on uremic toxins: classification, concentration, and interindividual variability. Kidney Int. 2003;63:1934–1943. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

