Phospholipases Dα and δ are involved in local and systemic wound responses of cotton (G. hirsutum)
- PMID: 28955998
- PMCID: PMC5614590
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2016.12.001
Phospholipases Dα and δ are involved in local and systemic wound responses of cotton (G. hirsutum)
Abstract
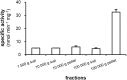
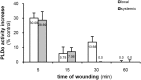
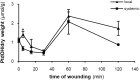
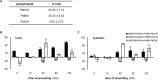
Phospholipases D (PLDs) catabolize structural phospholipids to produce phosphatidic acid (PtdOH), a lipid playing central role in signalling pathways in animal, yeast and plant cells. In animal cells two PLD genes have been studied while in model plant Arabidopsis twelve genes exist, classified in six classes (α-ζ). This underlines the role of these enzymes in plant responses to environmental stresses. However, information concerning the PLD involvement in the widely cultivated and economically important cotton plant responses is very limited. The aim of this report was to study the activity of conventional cotton PLD and its participation in plant responses to mechanical wounding, which resembles both biotic and abiotic stresses. PLDα activity was identified and further characterized by transphosphatidylation reaction. Upon wounding, cotton leaf responses consist of an acute in vitro increase of PLDα activity in both wounded and systemic tissue. However, determination of the in vivo PtdOH levels under the same wounding conditions revealed a rapid PtdOH formation only in wounded leaves and a late response of a PtdOH increase in both tissues. Εxpression analysis of PLDα and PLDδ isoforms showed mRNA accumulation of both isoforms in the wounded tissue, but only PLDδ exerts a high and sustainable expression in systemic leaves, indicating that this isoform is mainly responsible for the systemic wound-induced PtdOH production. Therefore, our data suggest that PLDα and PLDδ isoforms are involved in different steps in cotton wound signalling.
Keywords: Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum); HKD, catalytic motif; HRM, High Resolution Melting; PLD substrates; PLD, catalytic motif containing Histidine-Lysine-Aspartic acid residues; PLD, phospholipase D; PLDα and PLDδ; Phosphatidic acid; Phospholipase D activity; PtdCho, phosphatidylcholine; PtdEtOH, phosphatidylethanol; PtdEth, phosphatidylethanolamine; PtdOH, phosphatidic acid.; Wounding.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vivo substrates and the contribution of the common phospholipase D, PLDalpha, to wound-induced metabolism of lipids in Arabidopsis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001 Feb 26;1530(2-3):236-48. doi: 10.1016/s1388-1981(01)00091-9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001. PMID: 11239826
-
Study of the Involvement of Phosphatidic Acid Formation in the Expression of Wound-Responsive Genes in Cotton.Lipids. 2018 Jun;53(6):589-599. doi: 10.1002/lipd.12058. Epub 2018 Sep 10. Lipids. 2018. PMID: 30198579
-
Plant phospholipase D mining unravels new conserved residues important for catalytic activity.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2019 May;1864(5):688-703. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2019.01.008. Epub 2019 Jan 26. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2019. PMID: 30695732
-
Plant phospholipase D: novel structure, regulatory mechanism, and multifaceted functions with biotechnological application.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2022 Feb;42(1):106-124. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2021.1924113. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 34167393 Review.
-
Diacylglycerol, phosphatidic acid, and their metabolic enzymes in synaptic vesicle recycling.Adv Biol Regul. 2015 Jan;57:147-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2014.09.010. Epub 2014 Sep 28. Adv Biol Regul. 2015. PMID: 25446883 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization and evolutionary diversification of the phospholipase D gene family in mosses.Front Genet. 2022 Oct 13;13:1015393. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1015393. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36313445 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Testerink C., Munnik T. Phosphatidic acid: a multifunctional stress signaling lipid in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2005;10:368–375. - PubMed
-
- Wang X., Devaiah S.P., Zhang W., Welti R. Signaling functions of phosphatidic acid. Prog. Lipid Res. 2006;45:250–278. - PubMed
-
- Testerink C., Munnik T. Molecular, cellular, and physiological responses to phosphatidic acid formation in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2011;62:2349–2361. - PubMed
-
- Wang X. Phospholipase D in hormonal and stress signaling. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2002;5:408–414. - PubMed
-
- Bargmann B.O., Munnik T. The role of phospholipase D in plant stress responses. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2006;9:515–522. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

