Predicting the Global Potential Distribution of Four Endangered Panax Species in Middle-and Low-Latitude Regions of China by the Geographic Information System for Global Medicinal Plants (GMPGIS)
- PMID: 28956837
- PMCID: PMC6151741
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22101630
Predicting the Global Potential Distribution of Four Endangered Panax Species in Middle-and Low-Latitude Regions of China by the Geographic Information System for Global Medicinal Plants (GMPGIS)
Abstract
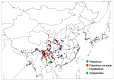
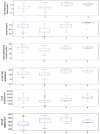
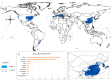
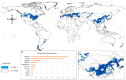
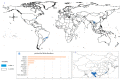
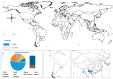
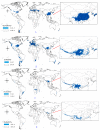
Global biodiversity is strongly influenced by the decrease in endangered biological species. Predicting the distribution of endangered medicinal plants is necessary for resource conservation. A spatial distribution model-geographic information system for global medicinal plants (GMPGIS)-is used to predict the global potential suitable distribution of four endangered Panax species, including Panax japonicas (T. Nees) C. A. Meyer and Panax japonicas var. major (Burkill) C. Y. Wu & K. M. Feng distributed in low- and middle-latitude, Panax zingiberensis C. Y. Wu & K. M. Feng and Panax stipuleanatus C. T. Tsai & K. M. Feng in low-latitude regions of China based on seven bioclimatic variables and 600 occurrence points. Results indicate that areas of P. japonicus and P. japonicusvar. major are 266.29 × 10⁵ and 77.5 × 10⁵ km², respectively, which are mainly distributed in China and America. By contrast, the areas of P. zingiberensis and P. stipuleanatus are 5.09 × 10⁵ and 2.05 × 10⁵ km², respectively, which are mainly distributed in Brazil and China. P. japonicus has the widest distribution among the four species. The data also indicate that the mean temperature of coldest quarter is the most critical factor. This scientific prediction can be used as reference for resource conservation of endangered plants and as a guide to search for endangered species in previously unknown areas.
Keywords: Panax; geographic information system for global medicinal plants (GMPGIS); global potential distribution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Rai A., Yamazaki M., Takahashi H., Nakamura M., Kojoma M., Suzuki H., Saito K. RNA-seq Transcriptome Analysis of Panax japonicus, and Its Comparison with Other Panax Species to Identify Potential Genes Involved in the Saponins Biosynthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2016;7:e0144. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00481. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

