Comparing biosimilar SB2 with reference infliximab after 54 weeks of a double-blind trial: clinical, structural and safety results
- PMID: 28957563
- PMCID: PMC5850768
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex254
Comparing biosimilar SB2 with reference infliximab after 54 weeks of a double-blind trial: clinical, structural and safety results
Abstract
Objectives: SB2 is a biosimilar to the reference infliximab (INF). Similar efficacy, safety and immunogenicity between SB2 and INF up to 30 weeks were previously reported. This report investigates such clinical similarity up to 54 weeks, including structural joint damage.
Methods: In this phase III, double-blind, parallel-group, multicentre study, patients with moderate to severe RA despite MTX were randomized (1:1) to receive 3 mg/kg of either SB2 or INF at 0, 2, 6 and every 8 weeks thereafter. Dose escalation by 1.5 mg/kg up to a maximum dose of 7.5 mg/kg was allowed after week 30. Efficacy, safety and immunogenicity were measured at each visit up to week 54. Radiographic damage evaluated by modified total Sharp score was measured at baseline and week 54.
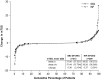
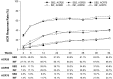
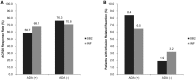
Results: A total of 584 patients were randomized to receive SB2 (n = 291) or INF (n = 293). The rate of radiographic progression was comparable between SB2 and INF (mean modified total Sharp score difference: SB2, 0.38; INF, 0.37) at 1 year. ACR responses, 28-joint DAS, Clinical Disease Activity Index and Simplified Disease Activity Index were comparable between SB2 and INF up to week 54. The incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events and anti-drug antibodies were comparable between treatment groups. Such comparable trends of efficacy, safety and immunogenicity were consistent from baseline up to 54 weeks. The pattern of dose increment was also comparable between SB2 and INF.
Conclusion: SB2 maintained similar efficacy, safety and immunogenicity with INF up to 54 weeks in patients with moderate to severe RA. Radiographic progression was comparable at 1 year.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov (http://clinicaltrials.gov; NCT01936181) and EudraCT (https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu; 2012-005733-37).
Keywords: Flixabi; Remicade; Renflexis; Sharp score; biosimilar; infliximab; monoclonal antibody; radiographic progression; rheumatoid arthritis; tumour necrosis factor blocker.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures

References
-
- Gossec L, Smolen JS, Ramiro S. et al. European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) recommendations for the management of psoriatic arthritis with pharmacological therapies: 2015 update. Ann Rheum Dis 2016;75:499–510. - PubMed
-
- Maini R, St Clair EW, Breedveld F. et al. Infliximab (chimeric anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving concomitant methotrexate: a randomised phase III trial. Lancet 1999;354:1932–9. - PubMed
-
- Weinblatt ME, Kremer JM, Bankhurst AD. et al. A trial of etanercept, a recombinant tumor necrosis factor receptor: Fc fusion protein, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving methotrexate. N Engl J Med 1999;340:253–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

