Discovery of imidazo[1,2-a]-, [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]-, and [1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyridine-8-carboxamide negative allosteric modulators of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5
- PMID: 28958625
- PMCID: PMC5716465
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2017.09.042
Discovery of imidazo[1,2-a]-, [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]-, and [1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyridine-8-carboxamide negative allosteric modulators of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5
Abstract
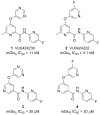
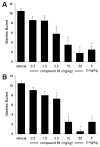
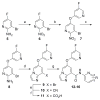
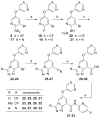
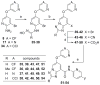
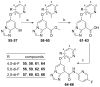
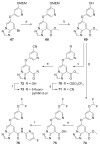
Based on a hypothesis that an intramolecular hydrogen bond was present in our lead series of picolinamide mGlu5 NAMs, we reasoned that an inactive nicotinamide series could be modified through introduction of a fused heterocyclic core to generate potent mGlu5 NAMs. In this Letter, we describe the synthesis and evaluation of compounds that demonstrate the viability of that approach. Selected analogs were profiled in a variety of in vitro assays, and two compounds were evaluated in rat pharmacokinetic studies and a mouse model of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Ancillary pharmacology screening revealed that members of this series exhibited moderate inhibition of the dopamine transporter (DAT), and SAR was developed that expanded the selectivity for mGlu5 versus DAT.
Keywords: Central nervous system (CNS); G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR); Heterocycle; Metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 (mGlu(5)); Negative allosteric modulator (NAM).
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Golubeva AV, Moloney RD, O’Connor RM, Dinan TG, Cryan JF. Curr Drug Targets. 2016;17:538. - PubMed
-
- Emmitte KA. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2017;27:691. - PubMed
-
- Berry-Kravis E, Des Portes V, Hagerman R, Jacquemont S, Charles P, Visootsak J, Brinkman M, Rerat K, Koumaras B, Zhu L, Barth GM, Jaecklin T, Apostol G, von Raison F. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8:321ra5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Miscellaneous

