Modification of population based arterial input function to incorporate individual variation
- PMID: 28958876
- PMCID: PMC5709187
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mri.2017.09.010
Modification of population based arterial input function to incorporate individual variation
Abstract
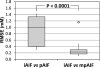
This technical note describes how to modify a population-based arterial input function to incorporate variation among the individuals. In DCE-MRI, an arterial input function (AIF) is often distorted by pulsated inflow effect and noise. A population-based AIF (pAIF) has high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), but cannot incorporate the individual variation. AIF variation is mainly induced by variation in cardiac output and blood volume of the individuals, which can be detected by the full width at half maximum (FWHM) during the first passage and the amplitude of AIF, respectively. Thus pAIF scaled in time and amplitude fitting to the individual AIF may serve as a high SNR AIF incorporating the individual variation. The proposed method was validated using DCE-MRI images of 18 prostate cancer patients. Root mean square error (RMSE) of pAIF from individual AIFs was 0.88±0.48mM (mean±SD), but it was reduced to 0.25±0.11mM after pAIF modification using the proposed method (p<0.0001).
Keywords: Arterial input function; DCE-MRI.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures





References
-
- Yankeelov TE, Rooney WD, Huang W, Dyke JP, Li X, Tudorica A, et al. Evidence for shutter-speed variation in CR bolus-tracking studies of human pathology. NMR Biomed. 2005;18(3):173–85. - PubMed
-
- Yankeelov TE, Rooney WD, Li X, Springer CS., Jr Variation of the relaxographic "shutter-speed" for transcytolemmal water exchange affects the CR bolus-tracking curve shape. Magn Reson Med. 2003;50(6):1151–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

