Quality of Life, Sexuality, Anatomical Results and Side-effects of Implantation of an Alloplastic Mesh for Cystocele Correction at Follow-up after 36 Months
- PMID: 28959063
- PMCID: PMC5612771
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0043-116857
Quality of Life, Sexuality, Anatomical Results and Side-effects of Implantation of an Alloplastic Mesh for Cystocele Correction at Follow-up after 36 Months
Abstract
Introduction: Pelvic organ prolapse can significantly reduce quality of life of affected women, with many cases requiring corrective surgery. The rate of recurrence is relatively high after conventional prolapse surgery. In recent years, alloplastic meshes have increasingly been implanted to stabilize the pelvic floor, which has led to considerable improvement of anatomical results. But the potential for mesh-induced risks has led to a controversial discussion on the use of surgical meshes in urogynecology. The impact of cystocele correction and implantation of an alloplastic mesh on patients' quality of life/sexuality and the long-term stability of this approach were investigated.
Method: In a large prospective multicenter study, 289 patients with symptomatic cystocele underwent surgery with implantation of a titanized polypropylene mesh (TiLOOP ® Total 6, pfm medical ag) and followed up for 36 months. Both primary procedures and procedures for recurrence were included in the study. Anatomical outcomes were quantified using the POP-Q system. Quality of life including sexuality were assessed using the German version of the validated P-QoL questionnaire. All adverse events were assessed by an independent clinical event committee.
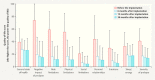
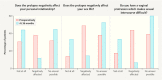
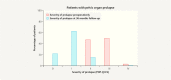
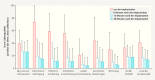
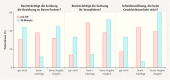
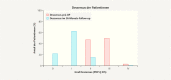
Results: Mean patient age was 67 ± 8 years. Quality of life improved significantly over the course of the study in all investigated areas, including sexuality and personal relationships (p < 0.001, Wilcoxon test). The number of adverse events which occurred in the period between 12 and 36 months after surgery was low, with just 22 events reported. The recurrence rate for the anterior compartment was 4.5%. Previous or concomitant hysterectomy increased the risk of recurrence in the posterior compartment 2.8-fold and increased the risk of erosion 2.25-fold.
Conclusion: Cystocele correction using a 2nd generation alloplastic mesh achieved good anatomical and functional results in cases requiring stabilization of the pelvic floor and in patients with recurrence. The rate of recurrence was low, the patients' quality of life improved significantly, and the risks were acceptable.
Einleitung Der Descensus genitalis kann die Lebensqualität erheblich einschränken. In vielen Fällen ist deshalb eine operative Korrektur erforderlich. Da die Rezidivrate bei der konventionellen Deszensuschirurgie recht hoch ist, wurden in den letzten Jahren zunehmend alloplastische Netze zur Stabilisierung eingesetzt. Die anatomischen Resultate konnten hierdurch deutlich verbessert werden. Die möglichen netzinduzierten Risiken haben zu einer kontroversen Diskussion über deren Einsatz geführt. In einer großen multizentrischen Studie wurde der Einfluss einer Netzimplantation zur Zystozelenkorrektur auf die Lebensqualität/Sexualität, und Langzeitstabilität untersucht. Methode 289 Patientinnen mit symptomatischer Zystozele wurden in einer prospektiven Studie mit einem titanisierten Polypropylennetz (TiLOOP ® Total 6, pfm medical ag) operiert und 36 Monate nachbeobachtet. Sowohl Primär- als auch Rezidiveingriffe wurden berücksichtigt. Das anatomische Resultat wurde mittels POP-Q-System quantifiziert. Die Lebensqualität inkl. Sexualität wurde mit dem validierten P-QoL-Fragebogen erfasst. Alle unerwünschten Ereignisse wurden von einem unabhängigen Komitee bewertet. Ergebnisse Das Durchschnittsalter der Patientinnen betrug 67 ± 8 Jahre. Die Lebensqualität verbesserte sich im Verlauf der Studie signifikant in allen untersuchten Bereichen, auch hinsichtlich der Sexualität und Partnerschaft (p < 0,001, Wilcoxon-Test). Die Anzahl unerwünschter Ereignisse zwischen 12 und 36 Monaten war mit 22 Meldungen gering. Die Rezidivrate im anterioren Kompartiment betrug 4,5%. Eine vorbestehende oder begleitend durchgeführte Hysterektomie erhöhte das Risiko eines Rezidivs im posterioren Kompartiment um das 2,8-Fache, das einer Erosion um das 2,25-Fache. Schlussfolgerung Die Zystozelenkorrektur mit einem alloplastischen Netz der 2. Generation erzielt in Fällen von gewünschter Stabilität oder in der Rezidivsituation ein gutes anatomisches und funktionelles Ergebnis. Die Rezidivrate ist gering, die Lebensqualität verbessert sich signifikant und die Risiken sind vertretbar.
Keywords: POP-Q; alloplastic mesh; pelvic organ prolapse; quality of life; sexuality.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Deutsche Gesellschaft für Gynäkologie und Geburtshilfe (DGGG) Arbeitsgemeinschaft der Wissenschaftlichen Medizinischen Fachgesellschaften (AWMF) Diagnostik und Therapie des weiblichen Descensus genitalis 2016. Online:http://www.awmf.org/uploads/tx_szleitlinien/015-006l_S2e_Descensus_genit...last access: 15.08.2017
-
- Mengel M, Henne B, Fünfgeld C. Entwicklung des Miktionsverhaltens unter Belastungsbedingungen und Lebensqualität nach netzgestützter Zystozelenkorrektur. Gynäkologische Praxis. 2015;39:10.
-
- Weber A M, Walters M D, Piedmonte M R. Sexual function and vaginal anatomy in women before and after surgery for pelvic organ prolapse and urinary incontinence. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000;182:1610–1615. - PubMed
-
- Fünfgeld C, Mengel M, Henne B. Zystozelenkorrektur mit alloplastischen Netzen. Frauenarzt. 2015;56:1068–1073.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

