An Image Fusion System for Estimating the Therapeutic Effects of Radiofrequency Ablation on Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 28959162
- PMCID: PMC5611990
- DOI: 10.1515/raon-2017-0028
An Image Fusion System for Estimating the Therapeutic Effects of Radiofrequency Ablation on Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
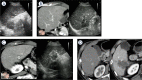
Background: During ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation (RFA) of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), high echoic areas due to RFA-induced microbubbles can help calculate the extent of ablation. However, these areas also decrease visualization of target tumors, making it difficult to assess whether they completely cover the tumors. To estimate the effects of RFA more precisely, we used an image fusion system (IFS).
Patients and methods: We enrolled patients with a single HCC who received RFA with or without the IFS. In the IFS group, we drew a spherical marker along the contour of a target tumor on reference images immediately after administering RFA so that the synchronized spherical marker represented the contour of the target tumor on real-time ultrasound images. When the high echoic area completely covered the marker, we considered the ablation to be complete. We compared outcomes between the IFS and control groups.
Results: We enrolled 25 patients and 20 controls, and the baseline characteristics were similar between the two groups. The complete ablation rates during the first RFA session were significantly higher in the IFS group compared with those in the control group (88.0% vs. 60.0%, P = 0.041). The number of RFA sessions was significantly smaller in the IFS group compared with that in the control group (1.1 ± 0.3 vs. 1.5 ± 0.7, P = 0.016).
Conclusions: The study suggested that the IFS enables a more precise estimation of the effects of RFA on HCC, contributing to enhanced treatment efficacy and minimized patient burden.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; image fusion; radiofrequency ablation.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Advanced ultrasonography technologies to assess the effects of radiofrequency ablation on hepatocellular carcinoma.Radiol Oncol. 2013 Jul 30;47(3):224-9. doi: 10.2478/raon-2013-0033. eCollection 2013. Radiol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24133386 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time US-CT/MR fusion imaging for percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma.J Hepatol. 2017 Feb;66(2):347-354. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.09.003. Epub 2016 Sep 17. J Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 27650284
-
Modified technique for determining therapeutic response to radiofrequency ablation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma using US-volume system.Oncol Rep. 2010 Feb;23(2):493-7. Oncol Rep. 2010. PMID: 20043112
-
Percutaneous image-guided radiofrequency ablation in the therapeutic management of hepatocellular carcinoma.Abdom Imaging. 2005 Jul-Aug;30(4):401-8. doi: 10.1007/s00261-004-0254-8. Abdom Imaging. 2005. PMID: 16132439 Review.
-
Real-time image fusion for successful percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma.J Ultrasound Med. 2014 Nov;33(11):2005-10. doi: 10.7863/ultra.33.11.2005. J Ultrasound Med. 2014. PMID: 25336489 Review.
Cited by
-
In vivo ultrasound thermal ablation control using echo decorrelation imaging in rabbit liver and VX2 tumor.PLoS One. 2019 Dec 5;14(12):e0226001. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226001. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31805129 Free PMC article.
-
Optimized Echo Decorrelation Imaging Feedback for Bulk Ultrasound Ablation Control.IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2018 Oct;65(10):1743-1755. doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2018.2847599. Epub 2018 Jun 14. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2018. PMID: 29994657 Free PMC article.
-
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound to ultrasound fusion during microwave ablation: feasibility study in a perfused porcine liver model.J Ultrasound. 2019 Sep;22(3):323-335. doi: 10.1007/s40477-019-00366-5. Epub 2019 Feb 27. J Ultrasound. 2019. PMID: 30811016 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time control of radiofrequency ablation using three-dimensional ultrasound echo decorrelation imaging in normal and diseasedex vivohuman liver.Phys Med Biol. 2025 Feb 5;70(4):10.1088/1361-6560/adaacb. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/adaacb. Phys Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 39813814 Free PMC article.
-
CT-guided Thermal Ablation of Liver Tumors Using Intraprocedural CT-CT Fusion for Applicator Position and Ablation Completeness Assessment: a Single-Center Comparative Analysis.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2025 Jul 10. doi: 10.1007/s00270-025-04111-w. Online ahead of print. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40640410
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
