Effects of combination therapy indacaterol/glycopyrronium versus tiotropium on moderate to severe COPD: evaluation of impulse oscillometry and exacerbation rate
- PMID: 28959443
- PMCID: PMC5615797
- DOI: 10.1186/s40248-017-0105-4
Effects of combination therapy indacaterol/glycopyrronium versus tiotropium on moderate to severe COPD: evaluation of impulse oscillometry and exacerbation rate
Abstract
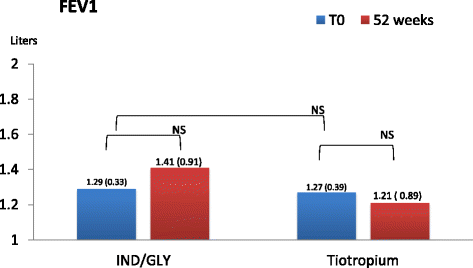
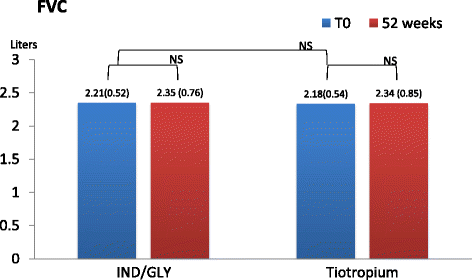
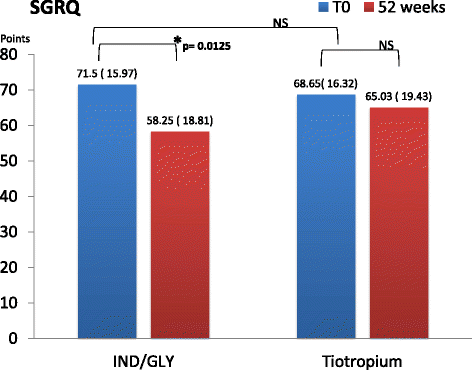
Background: Small airways are considered the major site of airflow limitation in COPD. Impulse oscillometry (IOS) is a forced oscillation technique, which provides passive measurement of lung mechanics. It can differentiate small airway from large airway obstruction and is more sensitive than spirometry for peripheral airway disease. In this study the efficacy of the combination of Indacaterol/Glycopirronium (IND/GLY) versus Tiotropium on airway resistance (R5, R20, R5-20), lung reactance (X) and resonant frequency in moderate to severe COPD patients has been evaluated. We also evaluated inspiratory capacity (IC), forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1), forced vital capacity (FVC), exacerbation rate and quality of life.
Methods: Forty patients were monitored with forced oscillation technique and spirometry. Patients were randomized in 2 groups: 20 received fixed dose once daily Indacaterol/Glycopyrronium (Group A) and 20 received single Tiotropium (Group B). The oscillometry parameters were the measure of resistance in the airways at 5 Hz (R5), at 20 Hz (R20) and the lung reactance (X).
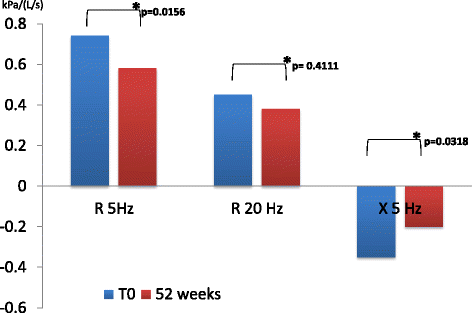
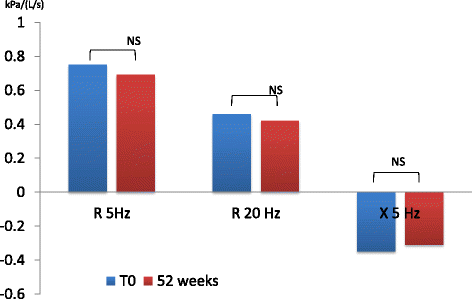
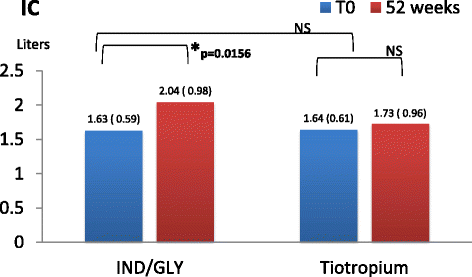
Results: There was a statistically significant difference between pre-dosing at V1 and at follow up visits in R5, R20 and X values in patients receiving dual bronchodilation but not in control group. Pre-dosing IC value at follow up visits in patients receiving dual bronchodilation had a statistical significant variation.
Conclusions: The "new" bronchodilator combination LABA/LAMA significantly reduces bronchial obstruction in small airways too. The oscillometry demonstrated greater sensitivity compared with spirometry for monitoring outcome measures of airway obstruction and the effect of long-term therapy.
Keywords: COPD; Impulse oscillometry lung function; Pulmonary function test; Small airway obstruction.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by Ethics Committee (SUN-AO Dei Colli, Naples, Italy) and all subjects gave their written informed consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Vogelmeier CF, Criner GJ, Martinez FJ, Anzueto A, Barnes PJ, Bourbeau J7 et al. Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease 2017 Report. GOLD Executive Summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195:557-82. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

