Apocynin reduced doxycycline-induced acute liver injury in ovariectomized mice
- PMID: 28959557
- PMCID: PMC5615834
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2016.02.003
Apocynin reduced doxycycline-induced acute liver injury in ovariectomized mice
Abstract
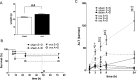
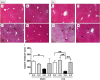
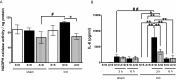
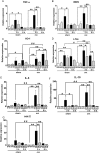
To determine the physiological role of estrogen in the development of liver injury, we examined the sensitivities of sham and ovariectomy (ovx) mice against doxycycline (DOXY)-induced acute liver injury. Ovx or sham operation was performed in C57BL/6J wild-type female mice of eight weeks of age. Sham mice and ovx mice were treated with DOXY (240 mg/kg ip) 8 weeks after the operation, 30 min after apocynin (5 mg/kg) or saline administration. Blood and liver samples were obtained at 3 and 6 h after DOXY administration. Liver dysfunction occurred soon after DOXY administration and became more severe in ovx mice than in sham mice. At early phase after DOXY injection, TNF-α and iNOS inductions upregulated almost the same levels in sham and ovx mice. On the other hand, expression levels of IL-6, IL-10, c-fos, cox-2 and HO-1, downstream genes of TNF-α, were significantly increased in ovx mice compared to those in sham mice, correlated with liver dysfunction. In addition, apocynin, a NADPH oxidase (Nox) inhibitor, totally improved DOXY-induced liver injury in both sham and ovx mice, indicating that reactive oxygen species generated through Nox activation by DOXY are responsible for development of acute liver injury.
Keywords: ALF, acute liver failure; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; ARF, acute renal failure; Apocynin; DOXY, doxycycline; Doxycycline-induced liver injury; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; IL-6, interleukin-6; NADPH oxidase; Nox, NADPH oxidase; Ovariectmized; Ovx, ovariectomy; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SOD, superoxide dismutase; STAT3, signal transducers and activators of transcription-3; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; cox-2, cyclooxygenase-2; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dimethylthiourea ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury in ovariectomized mice.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Aug;104:427-436. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.05.065. Epub 2018 May 25. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29787990
-
Raloxifene Ameliorates Liver Fibrosis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Induced by Choline-Deficient High-Fat Diet in Ovariectomized Mice.Dig Dis Sci. 2015 Sep;60(9):2730-9. doi: 10.1007/s10620-015-3660-6. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Dig Dis Sci. 2015. PMID: 25868633
-
Protective Effects of Tormentic Acid, a Major Component of Suspension Cultures of Eriobotrya japonica Cells, on Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice.Molecules. 2017 May 18;22(5):830. doi: 10.3390/molecules22050830. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28524081 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress induces vascular heme oxygenase-1 expression in ovariectomized rats.Free Radic Biol Med. 2005 Jul 1;39(1):108-17. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2005.02.033. Epub 2005 Mar 24. Free Radic Biol Med. 2005. PMID: 15925283
-
Severity of pancreatitis‑associated intestinal mucosal barrier injury is reduced following treatment with the NADPH oxidase inhibitor apocynin.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Oct;14(4):3525-34. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5678. Epub 2016 Aug 26. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27573037 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Effects of Apocynin on Monosodium Glutamate Induced Liver Damage of Rats.Heliyon. 2023 Jun 15;9(7):e17327. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17327. eCollection 2023 Jul. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37449146 Free PMC article.
-
Does apocynin increase liver regeneration in the partial hepatectomy model?Turk J Med Sci. 2023 Jun;53(3):647-658. doi: 10.55730/1300-0144.5627. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Turk J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37476910 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Role of Oxidative Stress and Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability as Injury Mechanisms in the Acute Pathophysiology of Blast-induced Neurotrauma.Sci Rep. 2019 May 22;9(1):7717. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44147-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31118451 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ayala A., Perrin M.M., Ertel W., Chaudry I.H. Differential effects of hemorrhage on kupffer cells: decreased antigen presentation despite increased inflammatory cytokine (Il-1, Il-6 and Tnf) release. Cytokine. 1992;4:66–75. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle P.A. Ikappab-Nf-kappab structures: at the interface of inflammation control. Cell. 1998;95:729–731. - PubMed
-
- Brenner C., Galluzzi L., Kepp O., Kroemer G. Decoding cell death signals in liver inflammation. J. Hepatol. 2013;59:583–594. - PubMed
-
- Fedchenko V., Globa A., Kaloshin A., Kapitsa I., Nerobkova L., Val’dman E., Buneeva O. The effect of short-term administration of (−)-deprenyl and isatin on the expressions of some genes in the mouse brain cortex. Med. Sci. Monit. 2008;14:BR269–BR273. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

