Bortezomib alters sour taste sensitivity in mice
- PMID: 28959638
- PMCID: PMC5615125
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2017.03.003
Bortezomib alters sour taste sensitivity in mice
Abstract
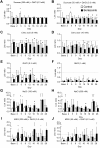
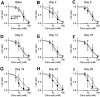
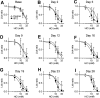
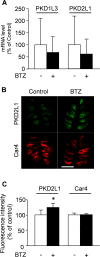
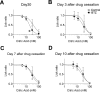
Chemotherapy-induced taste disorder is one of the critical issues in cancer therapy. Bortezomib, a proteasome inhibitor, is a key agent in multiple myeloma therapy, but it induces a taste disorder. In this study, we investigated the characteristics of bortezomib-induced taste disorder and the underlying mechanism in mice. Among the five basic tastes, the sour taste sensitivity of mice was significantly increased by bortezomib administration. In bortezomib-administered mice, protein expression of PKD2L1 was increased. The increased sour taste sensitivity induced by bortezomib returned to the control level on cessation of its administration. These results suggest that an increase in protein expression of PKD2L1 enhances the sour taste sensitivity in bortezomib-administered mice, and this alteration is reversed on cessation of its administration.
Keywords: AADC, aromatic amino acid decarboxylase; Adverse effect; BSA, bovine serum albumin; Bortezomib; CP, circumvallate papillae; Chemotherapy; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; HCl, hydrochloric acid; HE, hematoxylin-eosin; MSG, mono sodium glutamate; NaCl, sodium chloride; QHCl, quinine hydrochloride; Sour taste; Taste disorder.
Figures
References
-
- Hesketh P.J., Grunberg S.M., Gralla R.J., Warr D.G., Roila F., de Wit R., Chawla S.P., Carides A.D., Ianus J., Elmer M.E., Evans J.K., Beck K., Reines S., Horgan K.J. The oral neurokinin-1 antagonist aprepitant for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting: a multinational, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in patients receiving high-dose cisplatin-the Aprepitant Protocol 052 Study Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003;21:4112–4119. - PubMed
-
- Hesketh P.J. Chemotherapy-Induced nausea and vomiting. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008;358:2482–2494. - PubMed
-
- Halyard M.Y., Jatoi A., Sloan J.A., Bearden J.D., 3rd, Vora S.A., Atherton P.J., Perez E.A., Soori G., Zalduendo A.C., Zhu A., Stella P.J., Loprinzi C.L. Does zinc sulfate prevent therapy-induced taste alterations in head and neck cancer patients? Results of phase III double-blind, placebo-controlled trial from the North Central Cancer Treatment Group (N01C4) Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007;67:1318–1322. - PubMed
-
- Mukherjee N., Delay E.R. Cyclophosphamide-induced disruption of umami taste functions and taste epithelium. Neuroscience. 2011;192:732–745. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

