Yoga as part of a package of care versus standard care for schizophrenia
- PMID: 28960019
- PMCID: PMC6483611
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012145.pub2
Yoga as part of a package of care versus standard care for schizophrenia
Abstract
Background: Yoga is an ancient spiritual practice that originated in India and is currently accepted in the Western world as a form of relaxation and exercise. It has been of interest for people with schizophrenia to determine the efficacy of yoga delivered as a package of care versus standard care.
Objectives: To examine the effects of yoga as a package of care versus standard care.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group Trials Register (latest 30 March 2017) which is based on regular searches of MEDLINE, PubMed, Embase, CINAHL, BIOSS, AMED, PsychINFO, and registries of clinical trials. We searched the references of all included studies. There are no language, date, document type, or publication status limitations for inclusion of records in the register.
Selection criteria: All randomised controlled trials (RCTs) including people with schizophrenia comparing yoga as a package of care with standard-care control.
Data collection and analysis: The review authors independently selected studies, quality rated these, and extracted data. For binary outcomes, we calculated risk difference (RD) and its 95% confidence interval (CI), on an intention-to-treat (ITT) basis. For continuous data, we estimated the mean difference (MD) between groups and its CI. We employed mixed-effect and fixed-effect models for analysis. We examined heterogeneity (I2 technique), assessed risk of bias for included studies, and created a 'Summary of findings' table using GRADE (Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation).
Main results: Three studies are included in this review. All outcomes were short term (less than eight weeks). Useable data were reported for two outcomes only; leaving the study early and quality of life. None of the participants left the studies early and there was some evidence in favour of the yoga package for quality of life endpoint scores (1 RCT, n=80, MD 22.93 CI 19.74 to 26.12, low-quality evidence). Leaving the study early data were equivocal between the treatment groups (3 RCTs, n=193, RD 0.06 CI -0.01 to 0.13, medium-quality evidence, high heterogeneity). Overall, this review has an inordinate number of missing key outcomes, which included mental and global state, social functioning, physical health, adverse effects and costs of care.
Authors' conclusions: A small number of small studies were included in this review and these lacked many key outcomes. The sparse data means we cannot state with any degree of certainty if yoga delivered as a package of care is beneficial in comparison to standard care.
Conflict of interest statement
Julie Broderick ‐ none at time of writing the protocol or review.
Davy Vancampfort ‐ none at time of writing the protocol or review.
Figures
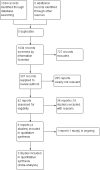
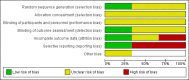




Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012145
References
References to studies included in this review
Isuru 2015 {published data only}
-
- Isuru LL, Dahanayake DMA, Alwis A, Weerasinghe A, Hewage SN, Ranasinghe CK. Impact of dance, drama, yoga and music therapy workshops on symptom reduction in patients with schizophrenia: A randomized controlled study. South Asian Journal of Psychiatry 2015;3:2, March:1‐7.
-
- SLCTR‐2013‐008 http://trials.slctr.lk/trials/113. Developing social skills, communication skills and self‐confidence through dance, drama and yoga in patients with long term mental illness at NIMH, Angoda. Trial Registry.
Paikkatt 2012 {published data only}
Xie 2006 {published data only}
-
- Xie J, Lin YH, Guo CR, Chen F. Study on influences of yoga on quality of life of schizophrenic inpatients [瑜伽练习对精神分裂症住院患者生活质量的影响]. Nanfang Journal of Nursing [南方护理学报] 2006;13:9‐10.
References to studies excluded from this review
Behere 2011 {published data only}
-
- Behere RV, Arasappa R, Jagannathan A, Varambally S, Venkatasubramanian G, Thirthalli J, et al. Effect of yoga therapy on facial emotion recognition deficits, symptoms and functioning in patients with schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 2011;123(2):147‐53. [PUBMED: 20846271] - PubMed
Bhatia 2012 {published data only}
Bhatia 2017 {published data only}
-
- Bhatia T, Mazumdar S, Wood J, Fanyin H, Gur RE, Gur R, et al. Adjunctive yoga or physical exercise can enhance cognitive functions among persons with schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin 2015;41:S69.
-
- Bhatia T, Mazumdar S, Wood J, He F, Gur RE, Gur RC, et al. Cognitive remediation with yoga for patients with schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015;40:S376.
Duraiswamy 2007 {published data only}
-
- Duraiswamy G, Thirthalli J, Nagendra HR, Gangadhar BN. Yoga therapy as an add‐on treatment in the management of patients with schizophrenia ‐ a randomized controlled trial. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 2007;116(3):226‐32. - PubMed
Hu 2014 {published data only}
-
- 胡光霞, 顾克鹏. 瑜伽练习对长春市某医院精神分裂症住院患者社会功能的影响. 医学与社会 2014;27(2):85‐7.
Ikai 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ikai S, Uchida H, Suzuki T, Tsunoda K, Mimura M, Fujii Y. Effects of yoga therapy on postural stability in patients with schizophrenia‐spectrum disorders: a single‐blind randomized controlled trial. Journal of Psychiatric Research 2013;47(11):1744‐50. [PUBMED: 23932244] - PubMed
Ikai 2014 {published data only}
-
- Ikai S, Suzuki T, Saruta J, Tsukinoki K, Tani H, Nagai N, et al. Effects of weekly one‐hour hatha yoga therapy on resilience and stress levels in schizophrenia: A randomized controlled eight‐week trial. Schizophrenia Bulletin 2015;41:S315‐6. - PubMed
-
- Ikai S, Suzuki T, Uchida H, Saruta J, Tsukinoki K, Fujii Y, et al. Effects of weekly one‐hour Hatha yoga therapy on resilience and stress levels in patients with schizophrenia‐spectrum disorders: an eight‐week randomized controlled trial. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine (New York, N.Y.) 2014;20(11):823‐30. [PUBMED: 25364946] - PubMed
Jayaram 2013 {published data only}
Kavak 2016 {published data only}
-
- Kavak F, Ekinci M. The effect of yoga on functional recovery level in schizophrenic patients. Archives of Psychiatric Nursing 2016;30(6):761‐7. - PubMed
Lin 2006 {published data only}
-
- Lin Y, Wang J, Xie J. Effectiveness of yoga alleviating side effects caused by antipsychotic medications [瑜珈健身法减轻抗精神病药物不良反应的效果观察]. Journal of Nursing Science [护理学杂志] 2006;21(3):56‐7.
Lin 2015 {published data only}
-
- Chen EYH, Lin J, Lee EHM, Chang WC, Chan SKW, Hui CLM. Yoga exercise for cognitive impairment in psychotic disorders. Schizophrenia Research 2014;153:S26.
-
- Chen EYH, Lin X, Lam MML, Chan KW, Chang WC, Joe G, et al. The impacts of yoga and aerobic exercise on neuro‐cognition and brain structure in early psychosis‐a preliminary analysis of the randomized controlled clinical trial. Schizophrenia Research 2012;136:S56.
-
- Lin J. The Impacts of Aerobic Exercise and Mind‐Body Exercise (Yoga) on Neuro‐cognition and Clinical Symptoms in Early Psychosis: A Single‐Blind Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial (Dissertation). The University of Hong Kong, 2013.
-
- Lin J. Yoga and exercise in psychosis (YEP). http://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT01207219 [Date Accessed: October 20, 2012].
Mahal 1976 {published data only}
-
- Mahal AS, Ramu NG, Chaturvedi DD. A double blind controlled study on the role of Brahmyadiyoga and Tagara in Navonmade (acute schizophrenia). Indian Journal of Psychiatry 1976;18(4):59‐88.
-
- Mahal AS, Ramu NG, Chaturvedi DD. Double blind controlled study of brahmyadiyoga and tagara in the management of various types of unmada (schizophrenia). Indian Journal of Psychiatry 1976;18(4):283‐92.
-
- Ramu MG, Chaturvedi DD, Venkataram BS, Shankara MR, Leelavathy S, Janakiramiah N, et al. A double blind controlled study on the role of brahmyadiyoga and tagara in navonmada (acute schizophrenia). Ayurvedic Management of Unmada (Schizophrenia). New Delhi, India: Central Council for Research in Ayurveda & Siddha, 1999:59‐88.
Manjunath 2013 {published data only}
Ramu 1999 {published data only}
-
- Ramu MG, Chaturvedi DD, Venkataram BS, Shankara MR, Leelavathy S, Janakiramiah N, et al. A double blind controlled study on the role of brahmyadiyoga and tagara in jirnomada (chronic schizophrenia). Ayurvedic Management of Unmada (Schizophrenia). Central Council for Research in Ayurveda and Siddha, 1999:77‐88.
Vancampfort 2011 {published data only}
-
- Vancampfort D, Hert M, Knapen J, Wampers M, Demunter H, Deckx S, et al. State anxiety, psychological stress and positive well‐being responses to yoga and aerobic exercise in people with schizophrenia: a pilot study. Disability and Rehabilitation 2011;33(8):684‐9. [PUBMED: 20718623] - PubMed
Varambally 2012 {published data only}
-
- Varambally S, Gangadhar BN, Thirthalli J, Jagannathan A, Kumar S, Venkatasubramanian G, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of add‐on yogasana intervention in stabilized outpatient schizophrenia: Randomized controlled comparison with exercise and waitlist. Indian Journal of Psychiatry 2012;54(3):227‐32. [PUBMED: 23226845] - PMC - PubMed
Varambally 2013 {published data only}
-
- CTRI‐2011‐06‐001792. Efficacy of brief yoga programme for caregivers of out‐patients with schizophrenia. http://www.ctri.nic.in/Clinicaltrials/pmaindet2.php?trialid=2838 [Date Accessed: May 20, 2011].
-
- Varambally S, Vidyendaran S, Sajjanar M, Thirthalli J, Hamza A, Nagendra HR, et al. Yoga‐based intervention for caregivers of outpatients with psychosis: a randomized controlled pilot study. Asian Journal of Psychiatry 2013;6(2):141‐5. - PubMed
Visceglia 2011 {published data only}
-
- Visceglia E, Lewis S. Yoga therapy as an adjunctive treatment for schizophrenia: a randomized, controlled pilot study. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine (New York, N.Y.) 2011;17(7):601‐7. [PUBMED: 21711202] - PubMed
Wu 2014 {published data only}
-
- 吴春芳, 王朔, 王文胜. 瑜伽训练对精神分裂症患者个人和社会功能的改善作用. 山东医药 2014;54(7):99‐100.
References to ongoing studies
JPRN‐UMIN000013746 {published data only}
-
- JPRN‐UMIN000013746. Effects study of yoga therapy on the association of mental illness with metabolic disorders, including the carbonyl stress. http://apps.who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=JPRN‐UMIN000013746 (accessed March 2015).
Additional references
Alford 1994
-
- Alford BA, Beck AT. Cognitive therapy of delusional beliefs. Behaviour Research and Therapy 1994;32(3):369‐80. [PUBMED: 8192636] - PubMed
Altman 1996
Bangalore 2012
Birchwood 2006
-
- Birchwood M, Trower P. The future of cognitive behavioural therapy for psychosis: not a quasi‐neuroleptic. British Journal of Psychiatry: The Journal of Mental Science 2006;188:107‐8. [PUBMED: 16449695] - PubMed
Bland 1997
Boissel 1999
-
- Boissel JP, Cucherat M, Li W, Chatellier G, Gueyffier F, Buyse M, et al. The problem of therapeutic efficacy indices, 3: comparison of the indices and their use [Apercu sur la problematique des indices d'efficacite therapeutique, 3: comparaison des indices et utilisation. Groupe d'Etude des Indices D'efficacite]. Therapie 1999;54(4):405‐11. [PUBMED: 10667106] - PubMed
Broderick 2015
Broderick 2016
Broderick 2017
Büssing 2012
Carbon 2014
-
- Carbon M, Correll CU. Thinking and acting beyond the positive: the role of the cognitive and negative symptoms in schizophrenia. CNS Spectrums 2014;19 Suppl 1:38‐52; quiz 35‐7, 53. [PUBMED: 25403863] - PubMed
Caspersen 1985
Collins 1998
-
- Collins C. Yoga: intuition, preventive medicine, and treatment. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, and Neonatal Nursing: JOGNN/NAACOG 1998;27(5):563‐8. [PUBMED: 9773368] - PubMed
Correll 2015
-
- Correll CU, Detraux J, Lepeleire J, Hert M. Effects of antipsychotics, antidepressants and mood stabilizers on risk for physical diseases in people with schizophrenia, depression and bipolar disorder. World Psychiatry: Official Journal of the World Psychiatric Association (WPA) 2015;14(2):119‐36. [PUBMED: 26043321] - PMC - PubMed
Cramer 2013
Crawford 2007
-
- Crawford MJ, Patterson S. Arts therapies for people with schizophrenia: an emerging evidence base. Evidence‐Based Mental Health 2007;10(3):69‐70. [PUBMED: 17652554] - PubMed
Damodaran 2002
-
- Damodaran A, Malathi A, Patil N, Shah N, Suryavansihi, Marathe S. Therapeutic potential of yoga practices in modifying cardiovascular risk profile in middle aged men and women. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India 2002;50(5):633‐40. - PubMed
Dauwan 2016
Deeks 2000
-
- Deeks J. Issues in the selection for meta‐analyses of binary data. Proceedings of the 8th International Cochrane Colloquium; 2000 Oct 25‐28. Cape Town: The Cochrane Collaboration, 2000.
Deeks 2011
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG (editors) on behalf of the Cochrane Statistical Methods Group. Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.handbook.cochrane.org.
Divine 1992
-
- Divine GW, Brown JT, Frazier LM. The unit of analysis error in studies about physicians' patient care behavior. Journal of General Internal Medicine 1992;7(6):623‐9. [PUBMED: 1453246] - PubMed
Donner 2002
-
- Donner A, Klar N. Issues in the meta‐analysis of cluster randomized trials. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21(19):2971‐80. [PUBMED: 12325113] - PubMed
Egger 1997
Elbourne 2002
-
- Elbourne D, Altman DG, Higgins JPT, Curtina F, Worthington HV, Vaile A. Meta‐analyses involving cross‐over trials: methodological issues. International Journal of Epidemiology 2002;31(1):140‐9. - PubMed
Elkins 2005
-
- Elkins G, Rajab MH, Marcus J. Complementary and alternative medicine use by psychiatric inpatients. Psychological Reports 2005;96(1):163‐6. [PUBMED: 15825920] - PubMed
Feifel 2011
-
- Feifel D. Is oxytocin a promising treatment for schizophrenia?. Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics 2011; Vol. 11, issue 2:157‐9. [PUBMED: 21306203] - PubMed
Furukawa 2006
-
- Furukawa TA, Barbui C, Cipriani A, Brambilla P, Watanabe N. Imputing missing standard deviations in meta‐analyses can provide accurate results. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2006;59(1):7‐10. [PUBMED: 16360555] - PubMed
Fusar‐Poli 2015
Geretsegger 2017
Global Burden of Disease 2015
-
- Global Burden of Disease Study 2013 Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990‐2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2015;386(9995):743‐800. - PMC - PubMed
Gulliford 1999
-
- Gulliford MC, Ukoumunne OC, Chinn S. Components of variance and intraclass correlations for the design of community‐based surveys and intervention studies: data from the Health Survey for England 1994. American Journal of Epidemiology 1999;149(9):876‐83. [PUBMED: 10221325] - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated September 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC (editors) on behalf of the Cochrane Statistical Methods Group and the Cochrane Bias Methods Group. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.handbook.cochrane.org.
Hutton 2009
-
- Hutton JL. Number needed to treat and number needed to harm are not the best way to report and assess the results of randomised clinical trials. British Journal of Haematology 2009;146(1):27‐30. [PUBMED: 19438480] - PubMed
Jones 2012
Kay 1986
-
- Kay SR, Opler LA, Fiszbein A. Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) Manual. North Tonawanda, NY: Multi‐Health Systems, 1986.
Kern 2009
Kimhy 2015
-
- Kimhy D, Vakhrusheva J, Bartels MN, Armstrong HF, Ballon JS, Khan S, et al. The impact of aerobic exercise on brain‐derived neurotrophic factor and neurocognition in individuals with schizophrenia: a single‐blind, randomized clinical trial. Schizophrenia Bulletin 2015;41(4):859‐68. [PUBMED: 25805886] - PMC - PubMed
Leon 2006
-
- Leon AC, Mallinckrodt CH, Chuang‐Stein C, Archibald DG, Archer GE, Chartier K. Attrition in randomized controlled clinical trials: methodological issues in psychopharmacology. Biological Psychiatry 2006;59(11):1001‐5. [PUBMED: 16905632] - PubMed
Leucht 2005
-
- Leucht S, Kane JM, Kissling W, Hamann J, Etschel E, Engel R. Clinical implications of brief psychiatric rating scale scores. British Journal of Psychiatry 2005;187:366‐71. [PUBMED: 16199797] - PubMed
Leucht 2013
-
- Leucht S, Cipriani A, Spineli L, Mavridis D, Orey D, Richter F, et al. Comparative efficacy and tolerability of 15 antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia: a multiple‐treatments meta‐analysis. Lancet (London, England) 2013;382(9896):951‐62. [PUBMED: 23810019] - PubMed
Li 1995
-
- Li LW, Wei H, Young D. The development of the General Quality of Life Inventory. China Mental Health Journal 1995;9:227‐31.
Li 1998
-
- Li L, Young D, Wei H. The relationship between objective life status and subjective life satisfaction with quality of life. Behavioral Medicine 1998;23(4):149‐59. - PubMed
Marshall 2000
-
- Marshall M, Lockwood A, Bradley C, Adams C, Joy C, Fenton M. Unpublished rating scales: a major source of bias in randomised controlled trials of treatments for schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 2000;176:249‐52. - PubMed
McGrath 2008
-
- McGrath J, Saha S, Chant D, Welham J. Schizophrenia: a concise overview of incidence, prevalence, and mortality. Epidemiologic Reviews 2008;30:67‐76. [PUBMED: 18480098] - PubMed
Moher 2001
-
- Moher D, Schulz KF, Altman D. The CONSORT statement: revised recommendations for improving the quality of reports of parallel‐group randomized trials. JAMA 2001;285(15):1987‐91. - PubMed
Nielsen 2015
-
- Nielsen RE, Levander S, Kjaersdam Telleus G, Jensen SO, Ostergaard Christensen T, Leucht S. Second‐generation antipsychotic effect on cognition in patients with schizophrenia ‐ a meta‐analysis of randomized clinical trials. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 2015;131(3):185‐96. [PUBMED: 25597383] - PubMed
Overall 1962
-
- Overall JE, Gorham DR. The Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale. Psychological Reports 1962;10:799‐812.
Owen 2016
Payne 2006
-
- Payne H. Dance Movement Therapy ‐ Theory, Research and Practice. 2nd Edition. Sussex: Routledge, 2006.
Ren 2013
Rolvsjord 2001
-
- Rolvsjord R. Sophie learns to play her songs of tears: a case study exploring the dialectics between didactic and psychotherapeutic music therapy practices. Nordic Journal of Music Therapy 2001;10(1):77‐85.
Ross 2012
Schünemann 2011
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, et al on behalf of the Cochrane Applicability and Recommendations Methods Group. Chapter 12: interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www. handbook.cochrane.org 2011.
Sherman 2012
Solli 2008
-
- Solli HP. “Shut up and play!” Improvisational use of popular music for a man with schizophrenia. Nordic Journal of Music Therapy 2008;17(1):67‐77.
Sterne 2011
-
- Sterne JAC, Egger M, Moher D (editors) on behalf of the Cochrane Bias Methods Group. Chapter 10: Addressing reporting biases. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Intervention. Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.handbook.cochrane.org.
Tandon 2013
-
- Tandon R, Gaebel W, Barch DM, Bustillo J, Gur RE, Heckers S, et al. Definition and description of schizophrenia in the DSM‐5. Schizophrenia Research 2013;150(1):3‐10. [PUBMED: 23800613] - PubMed
Tarrier 1993
-
- Tarrier N, Beckett R, Harwood S, Baker A, Yusupoff L, Ugarteburu I. A trial of two cognitive‐behavioural methods of treating drug‐resistant residual psychotic symptoms in schizophrenic patients: I. Outcome. British Journal of Psychiatry 1993;162:524‐32. [PUBMED: 8481745] - PubMed
Ukoumunne 1999
-
- Ukoumunne OC, Gulliford MC, Chinn S, Sterne JA, Burney PG. Methods for evaluating area‐wide and organisation‐based interventions in health and health care: a systematic review. Health Technology Assessment 1999;3(5):iii‐92. [PUBMED: 10982317] - PubMed
van Os 2009
-
- Os J, Kapur S. Schizophrenia. Lancet 2009;374(9690):635‐45. [PUBMED: 19700006] - PubMed
Vancampfort 2012
-
- Vancampfort D, Vansteelandt K, Scheewe T, Probst M, Knapen J, Herdt A, et al. Yoga in schizophrenia: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 2012;126(1):12‐20. [PUBMED: 22486714] - PubMed
Vancampfort 2014
-
- Vancampfort D, Probst M, Hert M, Soundy A, Stubbs B, Stroobants M, et al. Neurobiological effects of physical exercise in schizophrenia: a systematic review. Disability and Rehabilitation 2014;36(21):1749‐54. [PUBMED: 24383471] - PubMed
Vancampfort 2015
-
- Vancampfort D, Stubbs B, Mitchell AJ, Hert M, Wampers M, Ward PB, et al. Risk of metabolic syndrome and its components in people with schizophrenia and related psychotic disorders, bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. World Psychiatry: Official Journal of the World Psychiatric Association (WPA) 2015;14(3):339‐47. [PUBMED: 26407790] - PMC - PubMed
Verma 1989
-
- Verma SK, Verma A. Manual for PGI general well‐being measure. Lucknow: Ankur Psychological Agency 1989.
Xia 2009
-
- Xia J, Adams CE, Bhagat N, Bhagat V, Bhoopathi P, El‐Sayeh H, et al. Loss to outcomes stakeholder survey: the LOSS study. Psychiatric Bulletin 2009;33(7):254‐7.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

