Measurement of Fluid Status Using Bioimpedance Methods in Korean Pediatric Patients on Hemodialysis
- PMID: 28960036
- PMCID: PMC5639064
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.11.1828
Measurement of Fluid Status Using Bioimpedance Methods in Korean Pediatric Patients on Hemodialysis
Abstract
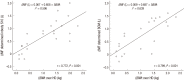
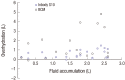
Adequate fluid management is an important therapeutic goal of dialysis. Recently, bioelectrical impedance methods have been used to determine body fluid status, but pediatric reports are rare. To determine the accuracy of bioelectrical impedance methods in the assessment of body fluid statusof children undergoing hemodialysis (HD), 12 children on HD were studied. A multi-frequency bioimpedance analysis device (Inbody S10) and bioimpedance spectroscopy device (BCM) were used to evaluate fluid status. Fluid removal during a HD session (assessed as body-weight change, ΔBWt) was compared with the difference in total body water determined by each device (measured fluid difference, ΔMF), which showed strong correlation using either method (Pearson's coefficient, r = 0.772 with Inbody S10 vs. 0.799 with BCM). Bioimpedance measurement indicated fluid overload (FO; ΔHS greater than 7%) in 34.8% with Inbody S10 and 56.5% with BCM, and only about 60% of children with FO by bioimpedance methods showed clinical symptoms such as hypertension and edema. In some patients with larger weight gain Inbody S10-assessed overhydration (OH) was much smaller than BCM-assessed OH, suggesting that BCM is more relevant in estimating fluid accumulation amount than Inbody S10. To our knowledge, this is the first report on the use of body composition monitors to assess fluid status in Korean children receiving HD.
Keywords: Bioimpedance; Children; Fluid Status; Hemodialysis.
© 2017 The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Frank Peacock W, Soto KM. Current technique of fluid status assessment. Congest Heart Fail. 2010;16(Suppl 1):S45–S51. - PubMed
-
- Kotanko P, Levin NW, Zhu F. Current state of bioimpedance technologies in dialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23:808–812. - PubMed
-
- Moissl UM, Wabel P, Chamney PW, Bosaeus I, Levin NW, Bosy-Westphal A, Korth O, Müller MJ, Ellegård L, Malmros V, et al. Body fluid volume determination via body composition spectroscopy in health and disease. Physiol Meas. 2006;27:921–933. - PubMed
-
- Ellis KJ, Shypailo RJ, Wong WW. Measurement of body water by multifrequency bioelectrical impedance spectroscopy in a multiethnic pediatric population. Am J Clin Nutr. 1999;70:847–853. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

