Bacterial cupredoxin azurin hijacks cellular signaling networks: Protein-protein interactions and cancer therapy
- PMID: 28960574
- PMCID: PMC5699490
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.3310
Bacterial cupredoxin azurin hijacks cellular signaling networks: Protein-protein interactions and cancer therapy
Abstract
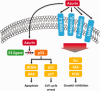
Azurin secreted by Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an anticancer bacteriocin, which preferentially enters human cancer cells and induces apoptosis or growth inhibition. It turns out that azurin is a multi-target anticancer agent interfering in the p53 signaling pathway and the non-receptor tyrosine kinases signaling pathway. This suggests that azurin exerts its anticancer activity by interacting with multiple targets and interfering in multiple steps in disease progression. Therefore, azurin could overcome resistance to therapy. Besides azurin, putative bacteriocins that possess functional properties similar to those of azurin have been identified in more bacteria species. A systematic investigation on the anticancer mechanisms of azurin and the azurin-like bacteriocins will provide more and better options in cancer therapy. In this review, we summarize how azurin and the derived peptides hijack key cellular regulators or cell surface receptors to remodel the cellular signaling networks. In particular, we highlight the necessity of determining the structure of azurin/p53 complex and investigating the influence of post-translational modifications on interactions between azurin and p53. Therapeutic applications of azurin and derived peptides are also discussed.
Keywords: Anticancer drugs; bacterial proteins; non-receptor tyrosine kinases; p53; tumor suppression.
© 2017 The Protein Society.
Figures


References
-
- van de Kamp M, Silvestrini MC, Brunori M, Van Beeumen J, Hali FC, Canters GW (1990) Involvement of the hydrophobic patch of azurin in the electron‐transfer reactions with cytochrome C551 and nitrite reductase. Eur J Biochem 194:109–118. - PubMed
-
- Fialho AM, Gupta TKD, Chakrabarty AM (2007) Designing promiscuous drugs? Look at what nature made!. Lett Drug Des Discov 4:40–43.
-
- Fialho AM, Bernardes N, Chakrabarty AM (2012) Recent patents on live bacteria and their products as potential anticancer agents. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov 7:31–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

