Small molecule signaling, regulation, and potential applications in cellular therapeutics
- PMID: 28960879
- PMCID: PMC5899512
- DOI: 10.1002/wsbm.1405
Small molecule signaling, regulation, and potential applications in cellular therapeutics
Abstract
Small molecules have many important roles across the tree of life: they regulate processes from metabolism to transcription, they enable signaling within and between species, and they serve as the biochemical building blocks for cells. They also represent valuable phenotypic endpoints that are promising for use as biomarkers of disease states. In the context of engineering cell-based therapeutics, they hold particularly great promise for enabling finer control over the therapeutic cells and allowing them to be responsive to extracellular cues. The natural signaling and regulatory functions of small molecules can be harnessed and rewired to control cell activity and delivery of therapeutic payloads, potentially increasing efficacy while decreasing toxicity. To that end, this review considers small molecule-mediated regulation and signaling in bacteria. We first discuss some of the most prominent applications and aspirations for responsive cell-based therapeutics. We then describe the transport, signaling, and regulation associated with three classes of molecules that may be exploited in the engineering of therapeutic bacteria: amino acids, fatty acids, and quorum-sensing signaling molecules. We also present examples of existing engineering efforts to generate cells that sense and respond to levels of different small molecules. Finally, we discuss future directions for how small molecule-mediated regulation could be harnessed for therapeutic applications, as well as some critical considerations for the ultimate success of such endeavors. WIREs Syst Biol Med 2018, 10:e1405. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.1405 This article is categorized under: Biological Mechanisms > Cell Signaling Biological Mechanisms > Metabolism Translational, Genomic, and Systems Medicine > Therapeutic Methods.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Monica P. McNerney, No conflicts of interest
Mark P. Styczynski, No conflicts of interest
Figures



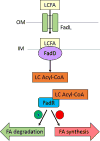

Similar articles
-
Stability analysis in spatial modeling of cell signaling.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2018 Jan;10(1). doi: 10.1002/wsbm.1395. Epub 2017 Aug 8. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2018. PMID: 28787545 Review.
-
Metabolism in cancer metastasis: bioenergetics, biosynthesis, and beyond.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2018 Mar;10(2). doi: 10.1002/wsbm.1406. Epub 2017 Oct 9. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2018. PMID: 28990735 Review.
-
More than a signal: non-signaling properties of quorum sensing molecules.Trends Microbiol. 2009 May;17(5):189-95. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2009.02.001. Epub 2009 Apr 15. Trends Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19375323 Review.
-
[Quorum sensing involved in the regulation of secondary metabolism in streptomycetes--a review].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2011 May;51(5):571-8. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2011. PMID: 21800617 Review. Chinese.
-
Quorum sensing and swarming migration in bacteria.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2004 Jun;28(3):261-89. doi: 10.1016/j.femsre.2003.09.004. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2004. PMID: 15449604 Review.
Cited by
-
Paromomycin targets HDAC1-mediated SUMOylation and IGF1R translocation in glioblastoma.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 11;15:1490878. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1490878. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39723246 Free PMC article.
-
Riboswitch Mechanisms: New Tricks for an Old Dog.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2021 Aug;86(8):962-975. doi: 10.1134/S0006297921080071. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2021. PMID: 34488573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined PARP inhibitors and small molecular inhibitors in solid tumor treatment (Review).Int J Oncol. 2023 Feb;62(2):28. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2023.5476. Epub 2023 Jan 5. Int J Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36601757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering Chemical Mediators Regulating Specialized Metabolism in a Symbiotic Cyanobacterium.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022 Jun 27;61(26):e202204545. doi: 10.1002/anie.202204545. Epub 2022 May 9. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022. PMID: 35403785 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics Analysis of the Toxic Effects of the Production of Lycopene and Its Precursors.Front Microbiol. 2018 May 3;9:760. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00760. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29774011 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Link H, Kochanowski K, Sauer U. Systematic identification of allosteric protein-metabolite interactions that control enzyme activity in vivo. Nature biotechnology. 2013;31:357–61. - PubMed
-
- Hofman-Bang J. Nitrogen catabolite repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biotechnol. 1999;12:35–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

