MRI-Guided Robotically Assisted Focal Laser Ablation of the Prostate Using Canine Cadavers
- PMID: 28961099
- PMCID: PMC8086175
- DOI: 10.1109/TBME.2017.2756907
MRI-Guided Robotically Assisted Focal Laser Ablation of the Prostate Using Canine Cadavers
Abstract
Objective: a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-conditional needle guidance robot is developed to enhance MRI-guided focal laser ablation (FLA) therapy in patients with focal prostate cancer.
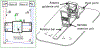
Methods: inspired by the workflow of the manual FLA therapy, we developed an MRI-conditional robot with two degrees of freedom to provide the guidance for laser ablation catheter. This robot is powered by pneumatic turbine motors and encoded with the custom-designed optical encoder. The needle could be inserted manually through the designed robotic system, which keeps the patients inside MRI bore throughout the procedure. The robot hardware is integrated with the custom ablation planning and monitoring software (OncoNav) to provide an iterative treatment plan to cover the whole ablation zone. Virtual tumors were selected in three canine cadavers as targets to validate the performance of the proposed hardware and software system.
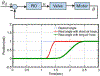
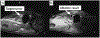
Results: phantom studies show that the average targeting error is less than 2 mm and the workflow of the entire procedure lasts for 100 minutes. Canine cadaver experiment results show that all the targets were successfully ablated in no more than three administrations.
Significance: MRI-guided prostate FLA is feasible using the proposed hardware and software system, indicating potential utility in future human trials.
Figures







References
-
- Siegel R et al., “Cancer statistics, 2017,” CA: Cancer J. Clin, vol. 67, pp. 7–30, 2017. - PubMed
-
- Visualase Image-Guided Thermal Laser Ablation Technology in Urology. [Online]. Available: http://www.visualaseinc.com/prostate-focal-ablation/. Accessed on: Mar. 17, 2014.
-
- Stoll M et al., “Transfer of methods from radiotherapy planning to ablation planning with focus on uncertainties and robustness,” Biomedical Engineering/Biomedizinische Technik 57.SI-1 Track-C, 2012, pp. 901–904.
-
- Lehmann KS et al., “In vivo validation of a therapy planning system for laser-induced thermotherapy (LITT) of liver malignancies,” Int. J. Colorectal Dis, vol. 26, pp. 799–808, 2011. - PubMed
-
- Cepek J et al., “Treatment planning for prostate focal laser ablation in the face of needle placement uncertainty,” Med. Phys, vol. 41, 2014, Art. no. 013301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

