In silico identification of rescue sites by double force scanning
- PMID: 28961796
- PMCID: PMC5860198
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx515
In silico identification of rescue sites by double force scanning
Abstract
Motivation: A deleterious amino acid change in a protein can be compensated by a second-site rescue mutation. These compensatory mechanisms can be mimicked by drugs. In particular, the location of rescue mutations can be used to identify protein regions that can be targeted by small molecules to reactivate a damaged mutant.
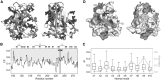
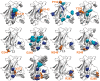
Results: We present the first general computational method to detect rescue sites. By mimicking the effect of mutations through the application of forces, the double force scanning (DFS) method identifies the second-site residues that make the protein structure most resilient to the effect of pathogenic mutations. We tested DFS predictions against two datasets containing experimentally validated and putative evolutionary-related rescue sites. A remarkably good agreement was found between predictions and experimental data. Indeed, almost half of the rescue sites in p53 was correctly predicted by DFS, with 65% of remaining sites in contact with DFS predictions. Similar results were found for other proteins in the evolutionary dataset.
Availability and implementation: The DFS code is available under GPL at https://fornililab.github.io/dfs/.
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
Figures
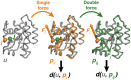

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

