Oral Delivery of Nanoparticles Loaded With Ginger Active Compound, 6-Shogaol, Attenuates Ulcerative Colitis and Promotes Wound Healing in a Murine Model of Ulcerative Colitis
- PMID: 28961808
- PMCID: PMC5881712
- DOI: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjx115
Oral Delivery of Nanoparticles Loaded With Ginger Active Compound, 6-Shogaol, Attenuates Ulcerative Colitis and Promotes Wound Healing in a Murine Model of Ulcerative Colitis
Abstract
Background and aims: Oral drug delivery is the most attractive pathway for ulcerative colitis [UC] therapy, since it has many advantages. However, this strategy has encountered many challenges, including the instability of drugs in the gastrointestinal tract [GT], low targeting of disease tissues, and severe adverse effects. Nanoparticles capable of colitis tissue-targeted delivery and site-specific drug release may offer a unique and therapeutically effective system that addresses these formidable challenges.
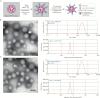
Methods: We used a versatile single-step surface-functionalising technique to prepare PLGA/PLA-PEG-FA nanoparticles loaded with the ginger active compound, 6-shogaol [NPs-PEG-FA/6-shogaol]. The therapeutic efficacy of NPs-PEG-FA/6-shogaol was evaluated in the well-established mouse model of dextran sulphate sodium [DSS]-induced colitis.
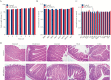
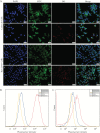
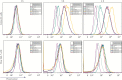
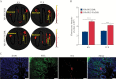
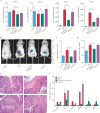
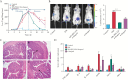
Results: NPs-PEG-FA exhibited very good biocompatibility both in vitro and in vivo. Subsequent cellular uptake experiments demonstrated that NPs-PEG-FA could undergo efficient receptor-mediated uptake by colon-26 cells and activated Raw 264.7 macrophage cells. In vivo, oral administration of NPs-PEG-FA/6-shogaol encapsulated in a hydrogel system [chitosan/alginate] significantly alleviated colitis symptoms and accelerated colitis wound repair in DSS-treated mice by regulating the expression levels of pro-inflammatory [TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and iNOS] and anti-inflammatory [Nrf-2 and HO-1] factors.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrates a convenient, orally administered 6-shogaol drug delivery system that effectively targets colitis tissue, alleviates colitis symptoms, and accelerates colitis wound repair. This system may represent a promising therapeutic approach for treating inflammatory bowel disease [IBD].
Keywords: Ulcerative colitis; drug delivery system; therapy.
Copyright © 2017 European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation (ECCO). Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com
Figures
Similar articles
-
Orally Targeted Delivery of Tripeptide KPV via Hyaluronic Acid-Functionalized Nanoparticles Efficiently Alleviates Ulcerative Colitis.Mol Ther. 2017 Jul 5;25(7):1628-1640. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2016.11.020. Epub 2017 Jan 28. Mol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28143741 Free PMC article.
-
Natural-lipid nanoparticle-based therapeutic approach to deliver 6-shogaol and its metabolites M2 and M13 to the colon to treat ulcerative colitis.J Control Release. 2020 Jul 10;323:293-310. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.04.032. Epub 2020 Apr 23. J Control Release. 2020. PMID: 32335157 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced therapeutic efficacy of a novel colon-specific nanosystem loading emodin on DSS-induced experimental colitis.Phytomedicine. 2020 Nov;78:153293. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153293. Epub 2020 Jul 25. Phytomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32777486
-
Paeoniflorin promotes intestinal stem cell-mediated epithelial regeneration and repair via PI3K-AKT-mTOR signalling in ulcerative colitis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Jun;119:110247. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110247. Epub 2023 May 7. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37159966 Review.
-
Application of chitosan/alginate nanoparticle in oral drug delivery systems: prospects and challenges.Drug Deliv. 2022 Dec;29(1):1142-1149. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2058646. Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 35384787 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prodrug Integrated Envelope on Probiotics to Enhance Target Therapy for Ulcerative Colitis.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Feb;10(4):e2205422. doi: 10.1002/advs.202205422. Epub 2022 Dec 11. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 36507607 Free PMC article.
-
6-Shogaol Inhibits Advanced Glycation End-Products-Induced IL-6 and ICAM-1 Expression by Regulating Oxidative Responses in Human Gingival Fibroblasts.Molecules. 2019 Oct 15;24(20):3705. doi: 10.3390/molecules24203705. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31619000 Free PMC article.
-
Oral administration of M13-loaded nanoliposomes is safe and effective to treat colitis-associated cancer in mice.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2023 Jul-Dec;20(10):1443-1462. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2023.2231345. Epub 2023 Jul 2. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2023. PMID: 37379034 Free PMC article.
-
Isoquinolinequinone Derivatives from a Marine Sponge (Haliclona sp.) Regulate Inflammation in In Vitro System of Intestine.Mar Drugs. 2021 Feb 4;19(2):90. doi: 10.3390/md19020090. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33557170 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 by traditional Chinese medicine drugs and their active ingredients.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 6;16:1604765. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1604765. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40548057 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- de Souza HS, Fiocchi C. Immunopathogenesis of IBD: current state of the art. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016;13:13–27. - PubMed
-
- Neurath MF. Current and emerging therapeutic targets for IBD. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017;14:269–78. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein CN. Treatment of IBD: where we are and where we are going. Am J Gastroenterol 2015;110:114–26. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

