A Computerized Microelectrode Recording to Magnetic Resonance Imaging Mapping System for Subthalamic Nucleus Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery
- PMID: 28961898
- PMCID: PMC6888019
- DOI: 10.1093/ons/opx169
A Computerized Microelectrode Recording to Magnetic Resonance Imaging Mapping System for Subthalamic Nucleus Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery
Abstract
Background: Accurate electrode placement is critical to the success of deep brain stimulation (DBS) surgery. Suboptimal targeting may arise from poor initial target localization, frame-based targeting error, or intraoperative brain shift. These uncertainties can make DBS surgery challenging.
Objective: To develop a computerized system to guide subthalamic nucleus (STN) DBS electrode localization and to estimate the trajectory of intraoperative microelectrode recording (MER) on magnetic resonance (MR) images algorithmically during DBS surgery.
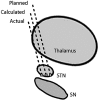
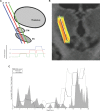
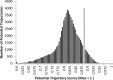
Methods: Our method is based upon the relationship between the high-frequency band (HFB; 500-2000 Hz) signal from MER and voxel intensity on MR images. The HFB profile along an MER trajectory recorded during surgery is compared to voxel intensity profiles along many potential trajectories in the region of the surgically planned trajectory. From these comparisons of HFB recordings and potential trajectories, an estimate of the MER trajectory is calculated. This calculated trajectory is then compared to actual trajectory, as estimated by postoperative high-resolution computed tomography.
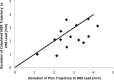
Results: We compared 20 planned, calculated, and actual trajectories in 13 patients who underwent STN DBS surgery. Targeting errors for our calculated trajectories (2.33 mm ± 0.2 mm) were significantly less than errors for surgically planned trajectories (2.83 mm ± 0.2 mm; P = .01), improving targeting prediction in 70% of individual cases (14/20). Moreover, in 4 of 4 initial MER trajectories that missed the STN, our method correctly indicated the required direction of targeting adjustment for the DBS lead to intersect the STN.
Conclusion: A computer-based algorithm simultaneously utilizing MER and MR information potentially eases electrode localization during STN DBS surgery.
Figures
References
-
- Benabid AL, Chabardes S, Mitrofanis J, Pollak P. Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8(1):67-81. - PubMed
-
- Krack P, Benazzouz A, Pollak Pet al. Treatment of tremor in Parkinson's disease by subthalamic nucleus stimulation. Mov Disord. 1998;13(6):907-914. - PubMed
-
- Benabid AL, Pollak P, Gross Cet al. Acute and long-term effects of subthalamic nucleus stimulation in Parkinson's disease. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 1994;62(1-4):76-84. - PubMed
-
- Krack P, Pollak P, Limousin P, Benazzouz A, Benabid AL. Stimulation of subthalamic nucleus alleviates tremor in Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 1997;350(9092):1675. - PubMed
-
- Kumar R, Lozano AM, Kim YJet al. Double-blind evaluation of subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation in advanced Parkinson's disease. Neurology. 1998;51(3):850-855. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

