Overexpression of TROP2 promotes proliferation and invasion of ovarian cancer cells
- PMID: 28962108
- PMCID: PMC5609167
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.4788
Overexpression of TROP2 promotes proliferation and invasion of ovarian cancer cells
Abstract
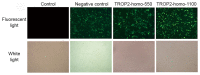
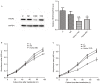
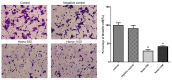
Human trophoblastic cell-surface marker, tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TROP2), is a newly identified marker that has a vital role in the proliferation and invasion of various tumors. However, its specific function in ovarian cancer has not been researched. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the role of TROP2 in the formation of ovarian cancer and its possible mechanism. TROP2 was knocked down by small interfering (si)RNA in ovarian cancer cell line, A2780. The expression of TROP2 protein following transfection was detected by western blot analysis. Cell viability was determined using a Cell Counting kit-8. Cancer cell migration and invasion were examined by wound healing and cell invasion assays, respectively. Apoptosis-related proteins, such as B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) and Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax), were measured by western blotting. Results demonstrated that the expression levels of TROP2 were markedly downregulated by siRNA in A2780 cells compared with the control groups, which led to strong inhibition of proliferation and invasion. Furthermore, TROP2 downregulation also reduced cell migratory ability. Additionally, in the TROP2-knockout group, Bcl-2 was downregulated and Bax was upregulated compared with the control. The present study suggested that the expression of TROP2 was related to cellular proliferation, migration and invasion. TROP2 may disrupt the balance in the Bax family to participate in apoptosis regulation in A2780 cells. Therefore, the overexpression of TROP2 may have a crucial role in tumorigenesis and tumor progression by disturbing the Bax/Bcl-2 balance in ovarian cancer.
Keywords: migration; ovarian cancer; proliferation; small interfering RNA; tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2.
Figures



References
-
- Fong D, Spizzo G, Gostner JM, Gastl G, Moser P, Krammel C, Gerhard S, Rasse M, Laimer K. TROP2: A novel prognostic marker in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. Mod Pathol. 2008;21:186–191. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
