Effect of the herbal formulation Shen-Zhi-Ling on an APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease by modulating the biliverdin reductase/heme oxygenase 1 system
- PMID: 28962110
- PMCID: PMC5609159
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.4732
Effect of the herbal formulation Shen-Zhi-Ling on an APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease by modulating the biliverdin reductase/heme oxygenase 1 system
Abstract
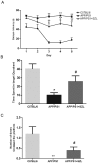
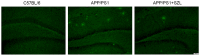
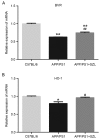
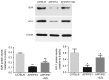
Shen-Zhi-Ling (SZL) oral liquid is a traditional Chinese medicine formula that is mainly used for the clinical treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease (AD). The aim of the present study was to investigate the effects and underlying mechanisms of SZL treatment on AD. APP/PS1 transgenic mice were utilized to evaluate the effect of SZL treatment (0.5 g/20 g/day). Morris water maze and Thioflavin S staining analyses were used to evaluate the cognitive impairment and β-amyloid plaques, respectively, while quantitative polymerase chain reaction and western blot analysis were performed to examine the mRNA and protein expression levels of heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1) and biliverdin reductase (BVR). Furthermore, immunofluorescence staining was used to measure the BVR and HO-1 protein levels in the hippocampus. The findings of the current study demonstrated that SZL treatment was able to ameliorate the impairment of memory and reduce the accumulation of amyloid plaques, and its ameliorating effects may be attributed to the modulation of the HO-1/BVR system in the hippocampus. These results indicate that SZL may be a possible complementary and alternative therapy to delay the development of AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Shen-Zhi-Ling oral liquid; biliverdin reductase; heme oxygenase 1.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Shen-Zhi-Ling oral liquid ameliorates cerebral glucose metabolism disorder in early AD via insulin signal transduction pathway in vivo and in vitro.Chin Med. 2021 Dec 2;16(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s13020-021-00540-0. Chin Med. 2021. PMID: 34857022 Free PMC article.
-
Shen-Zhi-Ling oral solution improves learning and memory ability in Alzheimer's disease mouse model.J Tradit Chin Med. 2019 Oct;39(5):667-677. J Tradit Chin Med. 2019. PMID: 32186116
-
Tiaoxin Recipe, a Chinese herbal formula, inhibits microRNA-34a expression in the APPswe/PS1ΔE9 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.J Integr Med. 2019 Nov;17(6):404-409. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2019.09.002. Epub 2019 Sep 9. J Integr Med. 2019. PMID: 31548147
-
Systematic Review of Basic Research on Alzheimer's Disease with Shen Zhi Ling Oral Liquid.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Apr 21;2019:8216714. doi: 10.1155/2019/8216714. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31118971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Heme Oxygenase/Biliverdin Reductase System as Effector of the Neuroprotective Outcomes of Herb-Based Nutritional Supplements.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Nov 11;10:1298. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01298. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31780933 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Jiedu-Yizhi Formula Improves Cognitive Impairment in an Aβ 25-35-Induced Rat Model of Alzheimer's Disease by Inhibiting Pyroptosis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Mar 16;2022:6091671. doi: 10.1155/2022/6091671. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35341145 Free PMC article.
-
Shenzhiling oral solution promotes myelin repair through PI3K/Akt-mTOR pathway in STZ-induced SAD mice.3 Biotech. 2021 Jul;11(7):361. doi: 10.1007/s13205-021-02900-x. Epub 2021 Jul 1. 3 Biotech. 2021. PMID: 34295606 Free PMC article.
-
Shen-Zhi-Ling oral liquid ameliorates cerebral glucose metabolism disorder in early AD via insulin signal transduction pathway in vivo and in vitro.Chin Med. 2021 Dec 2;16(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s13020-021-00540-0. Chin Med. 2021. PMID: 34857022 Free PMC article.
-
Bazhu Decoction, a Traditional Chinese Medical Formula, Ameliorates Cognitive Deficits in the 5xFAD Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Nov 27;10:1391. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01391. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31827437 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Winslow BT, Onysko MK, Stob CM, Hazlewood KA. Treatment of Alzheimer disease. Am Fam Physician. 2011;83:1403–1412. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
