Mislocalization of Runt-related transcription factor 3 results in airway inflammation and airway hyper-responsiveness in a murine asthma model
- PMID: 28962214
- PMCID: PMC5609286
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.4812
Mislocalization of Runt-related transcription factor 3 results in airway inflammation and airway hyper-responsiveness in a murine asthma model
Abstract
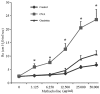
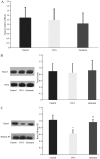
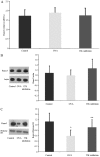
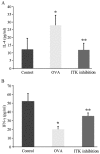
The Runt-related transcription factor (RUNX) gene family consists of three members, RUNX1, -2 and -3, which heterodimerize with a common protein, core-binding factor β, and contain the highly conserved Runt-homology domain. RUNX1 and -2 have essential roles in hematopoiesis and osteogenesis. Runx3 protein regulates cell lineage decisions in neurogenesis and thymopoiesis. The aim of the present study was to determine the expression features of the Runx3 protein in a murine asthma model. In vivo, Runx3 protein and mRNA were found to be almost equivalently expressed in the murine lung tissue of the control, ovalbumin (OVA) and genistein groups; however, the nuclear Runx3 protein was abated in lung tissue in OVA-immunized and challenged mice. Following treatment with genistein, which is a flavonoid previously demonstrated to decrease airway inflammation in asthma, the allergic airway inflammation and airway hyper-responsiveness were attenuated and the Runx3 protein tended to augment in the nucleus. These results were further determined in vitro. These results indicated that the mislocalization of Runx3 protein is a molecular mechanism of allergic inflammation and airway hyper-responsiveness in a murine asthma model.
Keywords: airway inflammation; asthma; genistein; interleukin-2-inducible T cell kinase inhibitor; runx3.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
