Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine binding to melanin: Some possible consequences for pathologies
- PMID: 28962308
- PMCID: PMC5598414
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2014.10.019
Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine binding to melanin: Some possible consequences for pathologies
Abstract
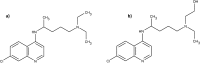
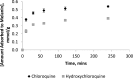
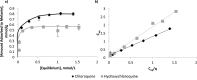
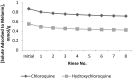
For many years chloroquine was used as a prophylactic agent against malaria, and more recently as a mild immunosuppressive. However, due to lengthy treatment periods, adverse effects have become apparent, which included retinopathy. The structurally related hydroxychloroquine is less toxic, thought to be owing to a lower tissue accumulation in melanin rich areas. This study primarily focused on quantifying melanin binding between chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine at physiological pH to investigate the potential link between binding and reported toxicity. In addition, for the first time this study quantified the actual extent of adsorption of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine to melanin and examined the desorption profile of both drugs from melanin to demonstrate the affinity between the pigment and the solutes. The results suggest that there is a difference between the adsorption affinities of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine, potentially explaining the differences in bioaccumulation in retinal tissue. In addition, both solutes displayed a strong physical attraction to the absorbent.
Keywords: Adsorption; Chloroquine; Desorption; Hydroxychloroquine; Melanin; Sepia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Physical factors affecting chloroquine binding to melanin.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015 Oct 1;134:8-16. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.06.040. Epub 2015 Jun 25. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015. PMID: 26141438
-
Retinal toxicity associated with hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine: risk factors, screening, and progression despite cessation of therapy.Arch Ophthalmol. 2011 Jan;129(1):30-9. doi: 10.1001/archophthalmol.2010.321. Arch Ophthalmol. 2011. PMID: 21220626
-
Binding of drugs to eye melanin is not predictive of ocular toxicity.Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 1998 Oct;28(2):124-32. doi: 10.1006/rtph.1998.1243. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9927562 Review.
-
[Chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine: variability of retinotoxic cumulative doses].Ophthalmologe. 2007 Oct;104(10):875-9. doi: 10.1007/s00347-007-1560-7. Ophthalmologe. 2007. PMID: 17653725 German.
-
Hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine: assessing the risk of retinal toxicity.J Am Optom Assoc. 1993 Nov;64(11):787-97. J Am Optom Assoc. 1993. PMID: 8120333 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic pitfalls and laboratory test interference after hydroxychloroquine intoxication: A case report.Toxicol Rep. 2019 Oct 7;6:1040-1046. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2019.10.006. eCollection 2019. Toxicol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31673506 Free PMC article.
-
Excessive lysosomal ion-trapping of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020 Jun;55(6):106007. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106007. Epub 2020 May 7. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020. PMID: 32389720 Free PMC article.
-
Do we have enough evidence to use chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine as a public health panacea for COVID-19?Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2020;75:e1928. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2020/e1928. Epub 2020 May 8. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2020. PMID: 32401962 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
4-Aminoquinoline compounds from the Spanish flu to COVID-19.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Mar;135:111138. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111138. Epub 2020 Dec 15. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33360781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitory effect of anti-malarial agents on the expression of proinflammatory chemokines via Toll-like receptor 3 signaling in human glomerular endothelial cells.Ren Fail. 2021 Dec;43(1):643-650. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2021.1908901. Ren Fail. 2021. PMID: 33820486 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bridelli M., Ciati A., Crippa P. Binding of chemicals to melanins re-examined – adsorption of some drugs to the surface of melanin particles. Biophys. Chem. 2006;119(2):137–145. - PubMed
-
- Bridelli M., Crippa P. Theoretical analysis of the adsorption of metal ions to the surface of melanin particles. Adsorption. 2008;14(1):101–109.
-
- Bridelli M.G., Ciati A., Crippa P.R. Binding of chemicals to melanins re-examined: adsorption of some drugs to the surface of melanin particles. Biophys. Chem. 2006;119(2):137–145. - PubMed
-
- Charkoudian L.K., Franz K.J. Fe(III)-coordination properties of neuromelanin components: 5,6-dihydroxyindole and 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic acid. Inorg. Chem. 2006;45(9):3657–3664. - PubMed
-
- Cooper R.G., Magwere T. Chloroquine: novel uses & manifestations. Indian J. Med. Res. 2008;127(4):305–316. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

