Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) supercritical CO2 extract derived withanolides mitigates Bisphenol A induced mitochondrial toxicity in HepG2 cells
- PMID: 28962313
- PMCID: PMC5598539
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2014.06.008
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) supercritical CO2 extract derived withanolides mitigates Bisphenol A induced mitochondrial toxicity in HepG2 cells
Abstract
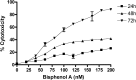
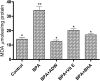
Bisphenol A (BPA) safety aspects on human health are debated extensively for long time. In the present study, we have studied the toxicity induced by BPA at no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL) using HepG2 cells. We report that BPA at 100 nM induced cytotoxicity to HepG2 cells as determined by MTT assay at 0-72 h. The toxicity was result of reduced oxygen consumption and reduced mitochondrial membrane potential associated with decreased ATP production. The BPA treatment resulted in increase of malondialdehyde (MDA) content with decreased glutathione and other antioxidant enzymes. BPA derived toxicity is a concern to human health and alternative non-toxic natural products/derivatives or adjuvants that serve as antidote will be relevant. In this context, Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) a widely used herb to treat arthritis, rheumatism and to improve longevity for time immemorial is investigated for its antidote effect. Ashwagandha supercritical CO2 extract derived Withanolides (ADW) at 100 μg/ml protect HepG2 cells from BPA induced toxicity by suppressing mitochondrial damage and increased ATP production. Further, cellular MDA content was significantly suppressed with increased non-enzymic and antioxidant enzyme activities. These findings derived from the present study suggest the beneficial effect of ADW in mitigating BPA induced mitochondrial toxicity in HepG2 cells.
Keywords: ADW, Ashwagandha supercritical CO2 extract derived Withanolides; Antioxidant enzymes; Ashwagandha; Bisphenol A; CAT, catalase; GPx, glutathione peroxidase; GSH, reduced glutathione; Glutathione; HepG2 cells; LPO, lipid peroxidation; MDA, malondialdehyde; Mitochondrial toxicity; SOD, superoxide dismutase; ΔΨM, mitochondrial membrane potential.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effects of bisphenol A on antioxidant system in soybean seedling roots.Environ Toxicol Chem. 2015 May;34(5):1127-33. doi: 10.1002/etc.2904. Epub 2015 Apr 7. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25651304
-
Lipoic acid mitigates bisphenol A-induced testicular mitochondrial toxicity in rats.Toxicol Ind Health. 2013 Nov;29(10):875-87. doi: 10.1177/0748233712446728. Epub 2012 May 23. Toxicol Ind Health. 2013. PMID: 22623521
-
Withania somnifera and Its Withanolides Attenuate Oxidative and Inflammatory Responses and Up-Regulate Antioxidant Responses in BV-2 Microglial Cells.Neuromolecular Med. 2016 Sep;18(3):241-52. doi: 10.1007/s12017-016-8411-0. Epub 2016 May 21. Neuromolecular Med. 2016. PMID: 27209361
-
Scientific basis for the therapeutic use of Withania somnifera (ashwagandha): a review.Altern Med Rev. 2000 Aug;5(4):334-46. Altern Med Rev. 2000. PMID: 10956379 Review.
-
Withania Somnifera (Ashwagandha) and Withaferin A: Potential in Integrative Oncology.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 25;20(21):5310. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215310. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31731424 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive review of medicinal plants and their beneficial roles in alleviating bisphenol A-induced organ toxicity.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jul;398(7):7801-7876. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03795-8. Epub 2025 Feb 11. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39932506 Review.
-
Neuroprotective effects of Withania somnifera in the SH-SY5Y Parkinson cell model.Heliyon. 2021 Oct 13;7(10):e08172. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08172. eCollection 2021 Oct. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 34765761 Free PMC article.
-
Re-evaluation of the risks to public health related to the presence of bisphenol A (BPA) in foodstuffs.EFSA J. 2023 Apr 19;21(4):e06857. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2023.6857. eCollection 2023 Apr. EFSA J. 2023. PMID: 37089179 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advancements in Extraction Techniques of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) with Insights on Phytochemicals, Structural Significance, Pharmacology, and Current Trends in Food Applications.ACS Omega. 2023 Oct 27;8(44):40982-41003. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c03491. eCollection 2023 Nov 7. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37970011 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ikezuki Y., Tsutsumi O., Takai Y., Kamei Y., Taketani Y. Determination of bisphenol A concentrations in human biological fluids reveals significant early prenatal exposure. Hum. Reprod. 2002;17:2839–2841. - PubMed
-
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) Statement of EFSA on a study associating bisphenol A with medical disorders. Eur. Food Saf. Auth. J. 2008;838:1–3.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

