Estrogen receptor α and aryl hydrocarbon receptor cross-talk in a transfected hepatoma cell line (HepG2) exposed to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin
- PMID: 28962316
- PMCID: PMC5598243
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2014.09.016
Estrogen receptor α and aryl hydrocarbon receptor cross-talk in a transfected hepatoma cell line (HepG2) exposed to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin
Abstract
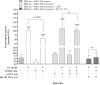
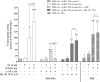
The prototype dioxin congener 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) is known to exert anti-estrogenic effects via activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) by interfering with the regulation of oestrogen homeostasis and the estrogen receptor α (ERα) signalling pathway. The AhR/ER cross-talk is considered to play a crucial role in TCDD- and E2-dependent mechanisms of carcinogenesis, though the concerted mechanism of action in the liver is not yet elucidated. The present study investigated TCDD's impact on the transcriptional cross-talk between AhR and ERα and its modulation by 17β-estradiol (E2) in the human hepatoma cell line HepG2, which is AhR-responsive but ERα-negative. Transient transfection assays with co-transfection of hERα and supplementation of receptor antagonists showed anti-estrogenic action of TCDD via down-regulation of E2-induced ERα signaling. In contrast, enhancement of AhR signaling dependent on ERα was observed providing evidence for increased cytochrome P450 (CYP) induction to promote E2 metabolism. However, relative mRNA levels of major E2-metabolizing CYP1A1 and 1B1 and the main E2-detoxifying catechol-O-methyltransferase were not affected by the co-treatments. This study provides new evidence of a TCDD-activated AhR-mediated molecular AhR/ERα cross-talk mechanism at transcriptional level via indirect inhibition of ERα and enhanced transcriptional activity of AhR in HepG2 cells.
Keywords: 17β-estradiol; AhR; AhR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; COMT, catechol-O-methyltransferase; CPRG, chlorophenol red β-d-galactopyranoside; CYP, cytochrome P450; Ct, cycle threshold; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; Dioxin; E, strogen receptor; E2, 17β-estradiol; ERE, estrogen response element; Estrogen receptor; Gene reporter assay; Human hepatoma cell line HepG2; TCDD; TCDD, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin; XRE, xenobiotic response element; α-NF, α-naphthoflavone.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dioxin and estrogen signaling in lung adenocarcinoma cells with different aryl hydrocarbon receptor/estrogen receptor α phenotypes.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013 Dec;49(6):1064-73. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0497OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23855798 Free PMC article.
-
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor interacts with estrogen receptor alpha and orphan receptors COUP-TFI and ERRalpha1.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000 Jan 1;373(1):163-74. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1999.1552. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000. PMID: 10620335
-
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated disruption of vitellogenin synthesis in the fish liver: Cross-talk between AHR- and ERalpha-signalling pathways.Comp Hepatol. 2004 May 2;3(1):2. doi: 10.1186/1476-5926-3-2. Comp Hepatol. 2004. PMID: 15119955 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of inhibitory aryl hydrocarbon receptor-estrogen receptor crosstalk in human breast cancer cells.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2000 Jul;5(3):295-306. doi: 10.1023/a:1009550912337. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2000. PMID: 14973392 Review.
-
Defining molecular sensors to assess long-term effects of pesticides on carcinogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Sep 25;15(9):17148-61. doi: 10.3390/ijms150917148. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25257533 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Implication of environmental estrogens on breast cancer treatment and progression.Toxicology. 2019 Jun 1;421:41-48. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2019.03.014. Epub 2019 Mar 30. Toxicology. 2019. PMID: 30940549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Menopause Hot Flashes and Molecular Mechanisms Modulated by Food-Derived Nutrients.Nutrients. 2024 Feb 26;16(5):655. doi: 10.3390/nu16050655. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38474783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Multi-Omics Study Revealing the Metabolic Effects of Estrogen in Liver Cancer Cells HepG2.Cells. 2021 Feb 20;10(2):455. doi: 10.3390/cells10020455. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33672651 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in mediating the effects of mono(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in mouse ovarian antral follicles†.Biol Reprod. 2024 Mar 13;110(3):632-641. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioad178. Biol Reprod. 2024. PMID: 38134965 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic role of antioxidants in rescuing delayed gastric emptying in high fat diet induced diabetic female mice.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 May;137:111370. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111370. Epub 2021 Feb 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33761597 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Swedenborg E., Pongratz I. AhR and ARNT modulate ER signaling. Toxicology. 2010;268:132–138. - PubMed
-
- Safe S., Wormke M. Inhibitory aryl hydrocarbon receptor-estrogen receptor alpha cross-talk and mechanisms of action. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2003;16:807–816. - PubMed
-
- Cavalieri E., Chakravarti D., Guttenplan J., Hart E., Ingle J., Jankowiak R., Muti P., Rogan E., Russo J., Santen R., Sutter T. Catechol estrogen quinones as initiators of breast and other human cancers: implications for biomarkers of susceptibility and cancer prevention. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2006;1766:63–78. - PubMed
-
- Knerr S., Schrenk D. Carcinogenicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in experimental models. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2006;50:897–907. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

