The effect of capsaicin on circulating biomarkers, soluble tumor necrosis factor and soluble tumor necrosis factor-receptor-1 and -2 levels in vivo using lipopolysaccharide-treated mice
- PMID: 28962318
- PMCID: PMC5598489
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2014.10.006
The effect of capsaicin on circulating biomarkers, soluble tumor necrosis factor and soluble tumor necrosis factor-receptor-1 and -2 levels in vivo using lipopolysaccharide-treated mice
Abstract
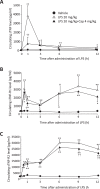
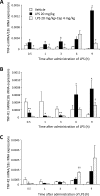
The circulating soluble tumor necrosis factor (sTNF) and sTNF-receptor (R) 1 and -R2 have known as septic biomarker. The pungent component of capsicum, capsaicin (Cap), has several associated physiological activities, including anti-oxidant, anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory effects. The aim of this study was to elucidate the effect of Cap on circulating sTNF and sTNF-R1 and -R2 in vivo using lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated mice. LPS (20 mg/kg, ip)-treated group was significantly increased circulating sTNF, sTNF-R1, and -R2 and TNF-α mRNA expression levels compared to the vehicle group. Treatment with LPS (20 mg/kg, ip) + Cap (4 mg/kg, sc)-treated group was significantly decreased both circulating sTNF levels (after 1 h only) and TNF-α mRNA expression (after 6 h) compared to the LPS-treated group. There is an early increase in circulating sTNF, sTNR-R1, and -R2 observed in the LPS-treated mice. Since Cap inhibits this initial increase as biomarkers, circulating sTNF, it is considered a potent treatment option for TNF-α-related diseases, such as septicemia. In conclusion, Cap interferes with TNF-α mRNA transcription and exerts an inhibiting effect on TNF-α release from macrophages in the early phase after LPS stimulation. Thus, Cap is considered a potent agent for the treatment of TNF-α-related diseases, such as septicemia.
Keywords: ADAM-17; Cap, capsaicin; Capsaicin; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; Lipopolysaccharide (LPS); NO, nitric oxide; PBS, phosphate buffered saline; Soluble tumor necrosis (sTNF); Soluble tumor necrosis factor-receptor 1 and 2 (TNF-R 1 and 2); TACE, TNF-converting enzyme; TNF-R, tumor necrosis factor-receptor; TNF-converting enzyme (TACE); TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chronological changes in circulating levels of soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors 1 and 2 in rats with carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury.Toxicology. 2014 Feb 28;316:55-60. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2013.12.004. Epub 2014 Jan 3. Toxicology. 2014. PMID: 24389507
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and Fas/Fas ligand signaling pathways in chronic spontaneous urticaria.Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2019 Mar 14;15:15. doi: 10.1186/s13223-019-0332-7. eCollection 2019. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30911316 Free PMC article.
-
Elevation of serum soluble tumour necrosis factor receptors in patients with polymyositis and dermatomyositis.Clin Rheumatol. 2000;19(5):352-9. doi: 10.1007/s100670070027. Clin Rheumatol. 2000. PMID: 11055823
-
Tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha)-converting enzyme (TACE) and soluble TNF-alpha receptor type 1 in psoriasis patients treated with narrowband ultraviolet B.Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2007 Aug;23(4):130-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0781.2007.00296.x. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2007. PMID: 17598866
-
Early detection of increased tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) and soluble TNF receptor protein plasma levels after trauma reveals associations with the clinical course.Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2001 Mar;45(3):364-70. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-6576.2001.045003364.x. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2001. PMID: 11207475
Cited by
-
Natural compounds and programmed necrosis: pioneering a new frontier in cancer treatments.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 26. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04050-w. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40137962 Review.
References
-
- Demirbilek S., Ersoy M.O., Demirbilek S., Karaman A., Gürbüz N., Bayraktar N., Bayraktar M. Small-dose capsaicin reduces systemic inflammatory responses in septic rats. Anesth. Analg. 2004;99(5):1501–1507. - PubMed
-
- Kalia N.P., Mahajan P., Mehra R., Nargotra A., Sharma J.P., Koul S., Khan I.A. Capsaicin, a novel inhibitor of the NorA efflux pump, reduces the intracellular invasion of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012;67(10):2401–2408. - PubMed
-
- Kim C.S., Kawada T., Kim B.S., Han I.S., Choe S.Y., Kurata T., Yu R. Capsaicin exhibits anti-inflammatory property by inhibiting IkB-a degradation in LPS-stimulated peritoneal macrophages. Cell. Signal. 2003;15:299–306. - PubMed
-
- Dunzendorfer S., Lee H.K., Soldau K., Tobias P.S. Toll-like receptor 4 functions intracellularly in human coronary artery endothelial cells: roles of LBP and sCD14 in mediating LPS responses. FASEB J. 2004;18:1117–1119. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

