Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor significantly decreases density of hippocampal caspase 3-positive nuclei, thus ameliorating apoptosis-mediated damage, in a model of ischaemic neonatal brain injury
- PMID: 28962511
- PMCID: PMC5886347
- DOI: 10.1093/icvts/ivx047
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor significantly decreases density of hippocampal caspase 3-positive nuclei, thus ameliorating apoptosis-mediated damage, in a model of ischaemic neonatal brain injury
Abstract
Objectives: Ischaemic brain injury is a major complication in patients undergoing surgery for congenital heart disease, with the hippocampus being a particularly vulnerable region. We hypothesized that neuronal injury resulting from cardiopulmonary bypass and associated circulatory arrest is ameliorated by pretreatment with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), a cytokine and an anti-apoptotic neurotrophic factor.
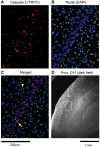
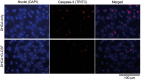
Methods: In a model of ischaemic brain injury, 4 male newborn piglets were anaesthetized and subjected to deep hypothermic circulatory arrest (DHCA) (cooled to 18°C, DHCA maintained for 60 min, rewarmed and recovered for 8-9 h), while 4 animals received G-CSF (34 µg/kg, intravenously) 2 h prior to the DHCA procedure. At the end of each experiment, the animals were perfused with a fixative, the hippocampus was extracted, cryoprotected, cut and the brain sections were immunoprocessed for activated caspase 3, a pro-apoptotic factor. Immunopositive neuronal nuclei were counted in multiple counting boxes (440 × 330 µm) centred on the CA1 or CA3 hippocampal regions and their mean numbers compared between the different treatment groups and regions.
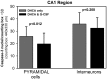
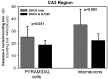
Results: G-CSF pretreatment resulted in significantly lower counts of caspase 3-positive nuclei per counting box in both the CA1 [52.2 ± 9.3 (SD) vs 61.6 ± 8.4, P < 0.001] and CA3 (41.2 ± 6.9 vs 60.4 ± 16.4, P < 0.00002) regions of the hippocampus as compared to DHCA groups. The effects of G-CSF were significant for pyramidal cells of both regions and for interneurons in the CA3 region.
Conclusions: In an animal model of ischaemic brain injury, G-CSF reduces neuronal injury in the hippocampus, thus potentially having beneficial effect on neurologic outcomes.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cardiac surgery; Caspase 3; Congenital heart disease; Developing brain; Hippocampus.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

