Long-term survival in patients treated with ruxolitinib for myelofibrosis: COMFORT-I and -II pooled analyses
- PMID: 28962635
- PMCID: PMC5622445
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-017-0527-7
Long-term survival in patients treated with ruxolitinib for myelofibrosis: COMFORT-I and -II pooled analyses
Abstract
Background: Myelofibrosis (MF) is associated with a variety of burdensome symptoms and reduced survival compared with age-/sex-matched controls. This analysis evaluated the long-term survival benefit with ruxolitinib, a Janus kinase (JAK)1/JAK2 inhibitor, in patients with intermediate-2 (int-2) or high-risk MF.
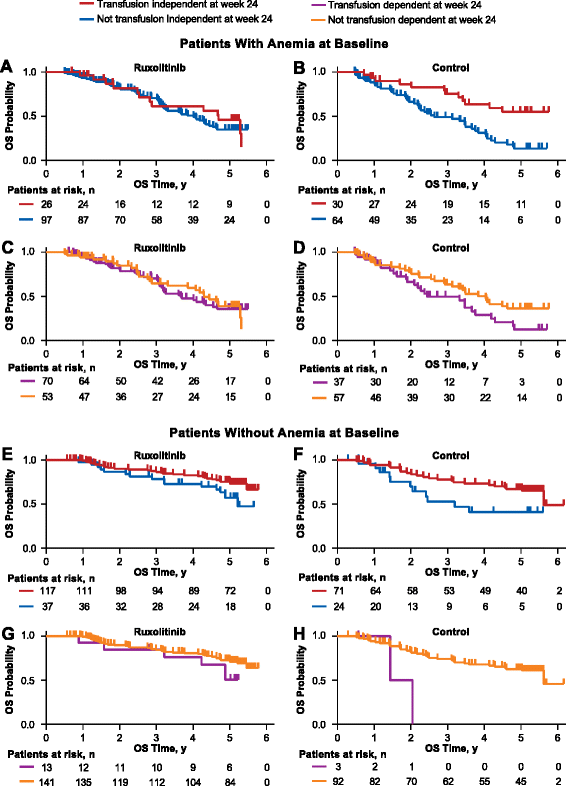
Methods: This was an exploratory analysis of 5-year data pooled from the phase 3 COMFORT-I and -II trials. In both trials, patients could cross over to ruxolitinib from the control group (COMFORT-I, placebo; COMFORT-II, best available therapy). All continuing patients in the control groups crossed over to ruxolitinib by the 3-year follow-up. Overall survival (OS; a secondary endpoint in both trials) was evaluated using pooled intent-to-treat data from patients randomized to ruxolitinib or the control groups. OS was also evaluated in subgroups stratified by baseline anemia and transfusion status at week 24.
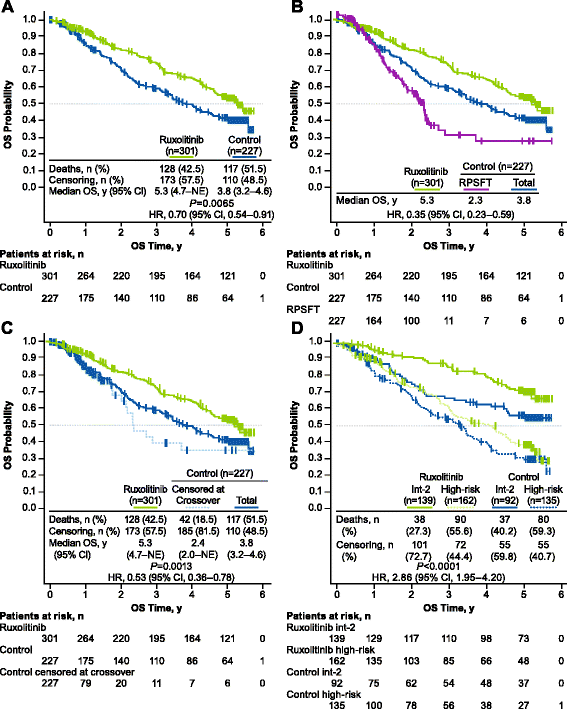
Results: A total of 528 patients were included in this analysis; 301 were originally randomized to ruxolitinib (COMFORT-I, n = 155; COMFORT-II, n = 146) and 227 to control (n = 154 and n = 73, respectively). The risk of death was reduced by 30% among patients randomized to ruxolitinib compared with patients in the control group (median OS, 5.3 vs 3.8 years, respectively; hazard ratio [HR], 0.70 [95% CI, 0.54-0.91]; P = 0.0065). After correcting for crossover using a rank-preserving structural failure time (RPSFT) method, the OS advantage was more pronounced for patients who were originally randomized to ruxolitinib compared with patients who crossed over from control to ruxolitinib (median OS, 5.3 vs 2.3 years; HR [ruxolitinib vs RPSFT], 0.35 [95% CI, 0.23-0.59]). An analysis of OS censoring patients at the time of crossover also demonstrated that ruxolitinib prolonged OS compared with control (median OS, 5.3 vs 2.4 years; HR [ruxolitinib vs censored at crossover], 0.53 [95% CI, 0.36-0.78]; P = 0.0013). The survival benefit with ruxolitinib was observed irrespective of baseline anemia status or transfusion requirements at week 24.
Conclusions: These findings support ruxolitinib treatment for patients with int-2 or high-risk MF, regardless of anemia or transfusion status. Further analyses will be important for exploring ruxolitinib earlier in the disease course to assess the effect on the natural history of MF.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov identifiers, NCT00952289 and NCT00934544 .
Keywords: Anemia; Myelofibrosis; Overall survival; Ruxolitinib; Transfusion.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Both trials (COMFORT-I and -II) were approved by the institutional review boards at each participating site and conducted in accordance with the International Conference on Harmonization guidelines for Good Clinical Practice. All patients provided written informed consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
SV has served on advisory boards for Incyte Corporation and received research funding for the conduct of clinical studies from Incyte Corporation, Roche, AstraZeneca, Lilly Oncology, Geron, NS Pharma, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Gilead, Seattle Genetics, Promedior, CTI BioPharma Corp, Galena BioPharma, Pfizer, and Genentech. JG has received honoraria and research funding from Incyte Corporation and served on an advisory committee for Incyte Corporation. RAM has received research funding from Incyte Corporation, Gilead, CTI BioPharma Corp, Promedior, and Celgene; he has served as a consultant for Novartis, Ariad, and Galena. AMV has received research funding from and served on advisory committees and speakers bureaus for Novartis. J-JK has received research funding from Novartis and AOP Orphan. FC has served on advisory committees for Novartis, Baxalta, and AOP Orphan and on speakers bureaus for Novartis and Baxalta. CNH has received honoraria from and served on speakers bureaus for Novartis, Shire, CTI BioPharma Corp, Gilead, Baxalta, and Incyte Corporation; served as a consultant for Novartis, CTI BioPharma, and Baxalta; and received research funding and reimbursement for travel accommodations or expenses from Novartis. RP served on speakers bureaus for and received research funding from Ariad, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Novartis. WS, AN, and PL are employees of and have equity ownership in Incyte Corporation. TD is an employee of and has equity ownership in Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation. PG is an employee of and has equity ownership in Novartis Pharma AG. VG has served as a consultant for and received research funding from Incyte Corporation and Novartis and has received honoraria from Novartis.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Hultcrantz M, Kristinsson SY, Andersson TM, Landgren O, Eloranta S, Derolf AR, et al. Patterns of survival among patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms diagnosed in Sweden from 1973 to 2008: a population-based study. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:2995–3001. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.42.1925. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cervantes F, Dupriez B, Pereira A, Passamonti F, Reilly JT, Morra E, et al. New prognostic scoring system for primary myelofibrosis based on a study of the International Working Group for Myelofibrosis Research and Treatment. Blood. 2009;113:2895–2901. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-07-170449. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gangat N, Caramazza D, Vaidya R, George G, Begna K, Schwager S, et al. DIPSS plus: a refined Dynamic International Prognostic Scoring System for primary myelofibrosis that incorporates prognostic information from karyotype, platelet count, and transfusion status. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:392–397. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.32.2446. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

