CNV-association meta-analysis in 191,161 European adults reveals new loci associated with anthropometric traits
- PMID: 28963451
- PMCID: PMC5622064
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-00556-x
CNV-association meta-analysis in 191,161 European adults reveals new loci associated with anthropometric traits
Abstract
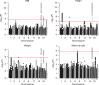
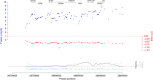
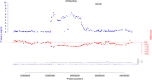
There are few examples of robust associations between rare copy number variants (CNVs) and complex continuous human traits. Here we present a large-scale CNV association meta-analysis on anthropometric traits in up to 191,161 adult samples from 26 cohorts. The study reveals five CNV associations at 1q21.1, 3q29, 7q11.23, 11p14.2, and 18q21.32 and confirms two known loci at 16p11.2 and 22q11.21, implicating at least one anthropometric trait. The discovered CNVs are recurrent and rare (0.01-0.2%), with large effects on height (>2.4 cm), weight (>5 kg), and body mass index (BMI) (>3.5 kg/m2). Burden analysis shows a 0.41 cm decrease in height, a 0.003 increase in waist-to-hip ratio and increase in BMI by 0.14 kg/m2 for each Mb of total deletion burden (P = 2.5 × 10-10, 6.0 × 10-5, and 2.9 × 10-3). Our study provides evidence that the same genes (e.g., MC4R, FIBIN, and FMO5) harbor both common and rare variants affecting body size and that anthropometric traits share genetic loci with developmental and psychiatric disorders.Individual SNPs have small effects on anthropometric traits, yet the impact of CNVs has remained largely unknown. Here, Kutalik and co-workers perform a large-scale genome-wide meta-analysis of structural variation and find rare CNVs associated with height, weight and BMI with large effect sizes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- G1001799/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/N01104X/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/N011317/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- S10 OD018522/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- MR/N01104X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 AG023749/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG023755/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_U127561128/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0902313/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 AG023746/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL117078/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 323195/ERC_/European Research Council/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

