Bupropion for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults
- PMID: 28965364
- PMCID: PMC6485546
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009504.pub2
Bupropion for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults
Abstract
Background: Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a prevalent neurobiological condition, characterised by behavioral and cognitive symptoms such as inattention, impulsivity and/or excessive activity. The syndrome is commonly accompanied by psychiatric comorbidities and is associated with educational and occupational underachievement.Although psychostimulant medications are the mainstay of treatment for ADHD, not all adults respond optimally to, or can tolerate, these medicines. Thus, alternative non-stimulant treatment approaches for ADHD have been explored. One of these alternatives is bupropion, an aminoketone antidepressant and non-competitive antagonism of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Bupropion is registered for the treatment of depression and smoking cessation, but is also used off-label to treat ADHD.
Objectives: To assess the effects and safety of bupropion for the treatment of adults with ADHD.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, Embase, and seven other databases in February 2017. We also searched three trials registers and three online theses portals. In addition, we checked references of included studies and contacted study authors to identify potentially relevant studies that were missed by our search.
Selection criteria: We included all randomised controlled trials (RCTs) that evaluated the effects (including adverse effects) of bupropion compared to placebo in adults with ADHD.
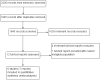
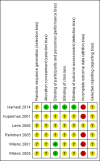
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors (WV, GB) independently screened records and extracted data using a data extraction sheet that we tested in a pilot study. We extracted all relevant data on study characteristics and results. We assessed risks of bias using the Cochrane 'Risk of bias' tool, and assessed the overall quality of evidence using the GRADE approach. We used a fixed-effect model to pool the results across studies.
Main results: We included six studies with a total of 438 participants. Five studies were conducted in the USA, and one in Iran. All studies evaluated a long-acting version of bupropion, with the dosage ranging from 150 mg up to 450 mg daily. Study intervention length varied from six to 10 weeks. Four studies explicitly excluded participants with psychiatric comorbidity and one study included only participants with opioid dependency. Four studies were funded by industry, but the impact of this on study results is unknown. Two studies were publicly funded and in one of these studies, the lead author was a consultant for several pharmaceutical companies and also received investigator-driven funding from two companies, however none of these companies manufacture bupropion. We judged none of the studies to be free of bias because for most risk of bias domains the study reports failed to provide sufficient details. Using the GRADE approach, we rated the overall quality of evidence as low. We downgraded the quality of the evidence because of serious risk of bias and serious imprecision due to small sample sizes.We found low-quality evidence that bupropion decreased the severity of ADHD symptoms (standardised mean difference -0.50, 95% confidence interval (CI) -0.86 to -0.15, 3 studies, 129 participants), and increased the proportion of participants achieving clinical improvement (risk ratio (RR) 1.50, 95% CI 1.13 to 1.99, 4 studies, 315 participants), and reporting an improvement on the Clinical Global Impression - Improvement scale (RR 1.78, 95% CI 1.27 to 2.50, 5 studies, 337 participants). There was low-quality evidence that the proportion of participants who withdrew due to any adverse effect was similar in the bupropion and placebo groups (RR 1.20, 95% CI 0.35 to 4.10, 3 studies, 253 participants). The results were very similar when using a random-effects model and when we analysed only studies that excluded participants with a psychiatric comorbidity.
Authors' conclusions: The findings of this review, which compared bupropion to placebo for adult ADHD, indicate a possible benefit of bupropion. We found low-quality evidence that bupropion decreased the severity of ADHD symptoms and moderately increased the proportion of participants achieving a significant clinical improvement in ADHD symptoms. Furthermore, we found low-quality evidence that the tolerability of bupropion is similar to that of placebo. In the pharmacological treatment of adults with ADHD, extended- or sustained-release bupropion may be an alternative to stimulants. The low-quality evidence indicates uncertainty with respect to the pooled effect estimates. Further research is very likely to change these estimates. More research is needed to reach more definite conclusions as well as clarifying the optimal target population for this medicine. Treatment response remains to be reported in a DSM5-diagnosed population. There is also a lack of knowledge on long-term outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
Wim Verbeeck ‐ none known. Geertruida E Bekkering ‐ none known. Wim Van den Noortgate ‐ none known. Cornelis Kramers ‐ none known.
Figures
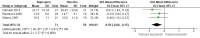



Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009504
References
References to studies included in this review
Hamedi 2014 {published data only}
-
- Hamedi M, Mohammadi M, Ghaleiha A, Keshavarzi Z, Jafarinia M, Keramatfar R, et al. Bupropion in adults with attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a randomized double‐blinded study. Acta Medica Iranica 2014;52(9):675‐80. [PUBMED: 25325205] - PubMed
Kuperman 2001 {published data only}
-
- Kuperman S [pers comm]. Reply to: Cochrane review [personal communication]. Email to: W Verbeeck 07 June 2016.
-
- Kuperman S, Perry PJ, Gaffney GR, Lund BC, Bever‐Stille KA, Arndt S, et al. Bupropion SR vs. methylphenidate vs. placebo for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in adults. Annals of Clinical Psychiatry 2001;13(3):129‐34. [PUBMED: 11791949] - PubMed
-
- Verbeeck W [pers comm]. Cochrane review [personal communication]. Email to: S Kuperman 05 June 2016.
Levin 2006 {published data only}
-
- Levin FR, Evans SM, Brooks DJ, Kalbag AS, Garawi F, Nunes EV. Treatment of methadone‐maintained patients with adult ADHD: double‐blind comparison of methylphenidate, bupropion and placebo. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2006;81(2):137‐48. [DOI: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2005.06.012; PUBMED: 16102908] - DOI - PubMed
Reimherr 2005 {published data only}
-
- Reimherr F [pers comm]. Reply to: Cochrane review [personal communication]. Email to: W Verbeeck 06 June 2016.
-
- Verbeeck W [pers comm]. Cochrane review [personal communication]. Email to: F Reimherr 05 June 2016.
Wilens 2001 {published data only}
Wilens 2005 {published data only}
-
- Hudziak JJ, Wilens TE, Connor DF, Haight BR, Horrigan JP, Hampton KD, et al. A controlled trial of extended‐release bupropion in adult ADHD. Biological Psychiatry 2004;8(Suppl):135S. - PubMed
-
- Wilens TE, Haight BR, Horrigan JP, Hudziak JJ, Rosenthal NE, Connor DF, et al. Bupropion XL in adults with attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a randomized, placebo‐controlled study. Biological Psychiatry 2005;57(7):793‐801. [DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.01.027; PUBMED: 15820237] - DOI - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Clay 1988 {published data only}
-
- Clay TH, Gualtieri CT, Evans RW, Gullion CM. Clinical and neuropsychological effects of the novel antidepressant bupropion. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1988;24(1):143‐8. [PUBMED: 3133717] - PubMed
Additional references
Adler 2008
APA 2000
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th Edition. Washington (DC): APA, 2000.
APA 2013
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM‐5®), Fifth Edition. Arlington (VA): American Psychiatric Publishing, 2013.
Argyelán 2005
-
- Argyelán M, Szabó Z, Kanyó B, Tanács A, Kovács Z, Janka Z, et al. Dopamine transporter availability in medication free and in bupropion treated depression: a 99mTc‐TRODAT‐1 SPECT study. Journal of Affective Disorders 2005;89(1‐3):115‐23. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jad.2005.08.016; PUBMED: 16213028] - DOI - PubMed
Arnsten 2005
Asherson 2005
Ashton 2006
Banerjee 2007
Baribeau 2013
Barkley 1990
-
- Barkley RA. Attention‐Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: a Handbook for Diagnosis and Treatment. New York: Guilford Press, 1990.
Berridge 2006
-
- Berridge CW, Devilbiss DM, Andrzejewski ME, Arnsten AF, Kelley AE, Schmeichel B, et al. Methylphenidate preferentially increases catecholamine neurotransmission within the prefrontal cortex at low doses that enhance cognitive function. Biological Psychiatry 2006;60(10):1111‐20. [DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.04.022; PUBMED: 16806100] - DOI - PubMed
Bidwell 2011
Biederman 2005
Biederman 2006
-
- Biederman J. Introduction: new developments in the treatment of attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2006;67(Suppl 8):4‐6. [PUBMED: 16961423] - PubMed
Bolea‐Alamañac 2014
-
- Bolea‐Alamañac B, Nutt DJ, Adamou M, Asherson P, Bazire S, Coghill D, et al. Evidence‐based guidelines for the pharmacological management of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: update on recommendations from the British Association for Psychopharmacology. Journal of Psychopharmacology 2014;28(3):179‐203. [DOI: 10.1177/0269881113519509; PUBMED: 24526134] - DOI - PubMed
Bush 2005
CADDRA 2011
-
- Canadian Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Resource Alliance (CADDRA). Canadian ADHD Practice Guidelines (CAP‐Guidlines), 3rd Edition. www.caddra.ca/practice‐guidelines (accessed prior to 30 May 2017).
CDC 2015
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Symptoms and diagnosis. www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/adhd/diagnosis.html (accessed 19 May 2015).
Conners 2003
-
- DeGeorge Macey K. Book review. Conners' adult ADHD rating scales (CAARS). Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology 2003;18(4):431‐7. [DOI: 10.1016/S0887-6177(03)00021-0] - DOI
Cunill 2015
Daviss 2001
-
- Daviss WB, Bentivoglio P, Racusin R, Brown KM, Bostic JQ, Wiley L. Bupropion sustained release in adolescents with comorbid attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder and depression. Journal of the American Academy of Child Adolescent Psychiatry 2001;40(3):307‐14. [DOI: 10.1097/00004583-200103000-00010; PUBMED: 11288772] - DOI - PubMed
Deeks 2011
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG, editor(s). Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Demyttenaere 2008
Dhillon 2008
-
- Dhillon S, Yang LP, Curran MP. Bupropion: a review of its use in the management of major depressive disorder. Drugs 2008;68(5):653‐89. [PUBMED: 18370448] - PubMed
Dopheide 2009
DuPaul 1990
-
- DuPaul GJ. The ADHD Rating Scale: Normative Data, Reliability, and Validity. Worchester (MA): University of Massachusetts Medical Center, 1990.
Egerton 2010
-
- Egerton A, Shotbolt JP, Stokes PR, Hirani E, Ahmad R, Lappin JM, et al. Acute effect of the anti‐addiction drug bupropion on extracellular dopamine concentrations in the human striatum: an [11C]raclopride PET study. Neuroimage 2010;50(1):260‐6. [DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.11.077; PMC4135078; PUBMED: 19969097] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Evins 2005
-
- Evins AE, Deckersbach T, Cather C, Freudenreich O, Culhane MA, Henderson DC, et al. Independent effects of tobacco abstinence and bupropion on cognitive function in schizophrenia. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2005;66(9):1184‐90. [PUBMED: 16187778] - PubMed
Faraone 1998
-
- Faraone SV, Biederman J. Neurobiology of attention‐deficit hyperactivity disorder. Biological Psychiatry 1998;44(10):951‐8. [PUBMED: 9821559] - PubMed
Faraone 2004
Faraone 2006
Faraone 2010
Fayyad 2007
Findling 2010
First 2013
-
- First MB. Comments: The National Institute of Mental Health Research Domain Criteria (RDoC) project: moving towards a neuroscience‐based diagnostic classification in psychiatry. In: Kendler KS, Parnas J editor(s). Philosophical Issues in Psychiatry II: Nosology. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2013:12‐8.
Gobbi 2003
Golden 1988a
-
- Golden RN, Rudorfer MV, Sherer MA, Linnoila M, Potter WZ. Bupropion in depression. I Biochemical effects and clinical response. Archives of General Psychiatry 1988;45(2):139‐43. [PUBMED: 3122698] - PubMed
Golden 1988b
-
- Golden RN, Vane CL, Laizure SC, Rudorfer MV, Sherer MA, Potter WZ. Bupropion in depression. II. The role of metabolites in clinical outcome. Archives of General Psychiatry 1988;45(2):145‐9. [PUBMED: 3122699] - PubMed
Goldman 1992
Greenhill 2002
-
- Greenhill LL, Pliszka S, Dulcan MK, Bernet W, Arnold V, Beitchman J, et al. Practice parameter for the use of stimulant medications in the treatment of children, adolescents, and adults. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2002;41(2 Suppl):26S‐49S. [PUBMED: 11833633] - PubMed
Guy 1976
-
- Guy W. Clinical global impressions. In: US Department of Health, Education, Welfare Public Health Service, Alcohol, Drug Abuse and Mental Health Administration, editor(s). ECDEU Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology. Rockville (MD): NIMH Psychopharmacology Research Branch, 1976:218‐222.
Guyatt 2011a
Guyatt 2011b
Guyatt 2011c
Guyatt 2011d
Hamilton 1960
Herrera‐Guzmán 2008
-
- Herrera‐Guzmán I, Gudayol‐Ferré E, Lira‐Mandujano J, Herrera‐Abarca J, Herrera‐Guzmán D, Montoya‐Pérez K, et al. Cognitive predictors of treatment response to bupropion and cognitive effects of bupropion in patients with major depressive disorder. Psychiatry Research 2008;160(1):72‐82. [DOI: 10.1016/j.psychres.2007.04.012; PUBMED: 18501971] - DOI - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC, editor(s). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Hilliard 2013
Himpel 2005
-
- Himpel S, Banaschewski T, Heise CA, Rothenberger A. The safety of non‐stimulant agents for the treatment of attention‐deficit hyperactivity disorder. Expert Opinion on Drug Safety 2005;4(2):311‐21. [PUBMED: 15794722] - PubMed
Hopewell 2009
Ilic 2013
-
- Ilic K, Hawke RL, Thirumaran RK, Schuetz EG, Hull JH, Kashuba AD, et al. The influence of sex, ethnicity, and CYP2B6 genotype on bupropion metabolism as an index of hepatic CYP2B6 activity in humans. Drug Metabolism and Disposition 2013;41(3):575‐81. [DOI: 10.1124/dmd.112.048108; PMC4162003] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Jefferson 2005
Kooij 2010
Lamba 2003
-
- Lamba V, Lamba J, Yasuda K, Strom S, Davila J, Hancock ML, et al. Hepatic CYP2B6 expression: gender and ethnic differences and relationship to CYP2B6 genotype and CAR (Constitutive Androstane Receptor) expression. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 2003;307(3):906‐22. [DOI: 10.1124/jpet.103.054866; PUBMED: 14551287] - DOI - PubMed
Learned‐Coughlin 2003
-
- Learned‐Coughlin SM, Bergström M, Savitcheva I, Ascher J, Schmith VD, Långstrom B. In vivo activity of bupropion at the human dopamine transporter as measured by positron emission tomography. Biological Psychiatry 2003;54(8):800‐5. [PUBMED: 14550679] - PubMed
Leonard 2004
Lexchin 2003
Maier 1988
-
- Maier W, Buller R, Philipp M, Heuser I. The Hamilton Anxiety Scale: reliability, validity and sensitivity to change in anxiety and depressive disorders. Journal of Affective Disorders 1988;14(1):61‐8. [PUBMED: 2963053] - PubMed
Maneeton 2011
-
- Maneeton N, Maneeton B, Srisurapanont M, Martin SD. Bupropion for adults with attention‐deficit hyperactivity disorder: meta‐analysis of randomized, placebo‐controlled trials. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences 2011;65(7):611‐7. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1819.2011.02264.x; PUBMED: 22176279] - DOI - PubMed
Maneeton 2014
-
- Maneeton N, Maneeton B, Intaprasert S, Woottiluk P. A systematic review of randomized controlled trials of bupropion versus methylphenidate in the treatment of attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment 2014;10:1439‐49. [DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S62714; PMC4128852; PUBMED: 25120365] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Marchant 2013
Matte 2015
Mehta 2000
Meyer 2002
Moher 2009
Moriyama 2013
Murphy 1996
-
- Murphy K, Barkley RA. Prevalence of DSM‐IV symptoms of ADHD in adult licensed drivers: implications for clinical diagnosis. Journal of Attention Disorders 1996;1(3):147‐61. [DOI: 10.1177/108705479600100303] - DOI
Newcorn 2008a
Newcorn 2008b
-
- Newcorn JH, Kratochvil CJ, Allen AJ, Casat CD, Ruff DD, Moore RJ, et al. Atomoxetine/Methylphenidate Comparative Study Group. Atomoxetine and osmotically released methylphenidate for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: acute comparison and differential response. American Journal of Psychiatry 2008;165(6):721‐30. [DOI: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2007.05091676; PUBMED: 18281409] - DOI - PubMed
NICE 2008
-
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: diagnosis and management of ADHD in children, young people and adults (NICE guidelines CG72). www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg72 (accessed 19 May 2015).
NIMH 1984
-
- National Institute of Mental Health. CGI (Clinical Global Impression Scale). Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1985;21:839‐44.
Nutt 2007
-
- Nutt DJ, Fone K, Asherson P, Bramble D, Hill P, Matthews K, et al. British Association for Psychopharmacology. Evidence‐based guidelines for management of attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adolescents in transition to adult services and in adults: recommendations from the British Association for Psychopharmacology. Journal of Psychopharmacology 2007;21(1):10‐41. [DOI: 10.1177/0269881106073219; PUBMED: 17092962] - DOI - PubMed
Oppek 2014
Peterson 2008
-
- Peterson K, McDonagh MS, Fu R. Comparative benefits and harms of competing medications for adults with attention‐deficit hyperactivity disorder: a systematic review and indirect comparison meta‐analysis. Psychopharmacology 2008;197(1):1‐11. [DOI: 10.1007/s00213-007-0996-4; PUBMED: 18026719] - DOI - PubMed
Pisani 2002
-
- Pisani F, Oteri G, Costa C, Raimondo G, Perri R. Effects of psychotropic drugs on seizure threshold. Drug Safety 2002;25(2):91‐110. [PUBMED: 11888352] - PubMed
Pliszka 2003
-
- Pliszka SR. Non‐stimulant treatment of attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder. CNS Spectrums 2003;8(4):253‐8. [PUBMED: 12679740] - PubMed
Popper 1997
-
- Popper CW. Antidepressants in the treatment of ADHD. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1997;58(Suppl 14):14‐29. [PUBMED: 9418743] - PubMed
Prosser 2013
Rapoport 2002
-
- Rapoport JL, Inoff‐Germain G. Responses to methylphenidate in Attention‐Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and normal children: update 2002. Journal of Attention Disorders 2002;6(Suppl 1):S57‐60. [PUBMED: 12685519] - PubMed
Rostain 2008
Sarampote 2004
Schünemann 2013
-
- Schünemann H, Brożek J, Guyatt G, Oxman A, GRADE Working Group. GRADE handbook for grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. www.guidelinedevelopment.org/handbook. (accessed prior to 30 May 2017).
Sibley 2013
Solhkhah 2005
-
- Solhkhah R, Wilens TE, Daly J, Prince JB, Patten SL, Biederman J. Bupropion SR for the treatment of substance‐abusing outpatient adolescents with attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder and mood disorders. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology 2005;15(5):777‐86. [DOI: 10.1089/cap.2005.15.777; PUBMED: 16262594] - DOI - PubMed
Sonuga‐Barke 2005
Spencer 2004
Spencer 2005
-
- Spencer T, Biederman J, Wilens T, Doyle R, Surman C, Prince J, et al. A large, double‐blind, randomized clinical trial of methylphenidate in the treatment of adults with attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biological Psychiatry 2005;57(5):456‐63. [DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.11.043; PUBMED: 15737659] - DOI - PubMed
Steinhausen 2009
Storebø 2015
Swanson 2003
-
- Swanson JM, Volkow ND. Serum and brain concentrations of methylphenidate: implications for use and abuse. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews 2003;27(7):615‐21. [PUBMED: 14624806] - PubMed
Van den Noortgate 2003
-
- Noortgate W, Onghena P. Multilevel meta‐analysis: a comparison with traditional meta‐analytical procedures. Educational and Psychological Measurement 2003;63(5):765‐90. [DOI: 10.1177/0013164403251027] - DOI
Vaughan 2008
Voeller 2004
Volkow 1995
-
- Volkow ND, Ding Y, Fowler JS, Wang GJ, Logan J, Gatley JS, et al. Is methylphenidate like cocaine? Studies on their pharmacokinetics and distribution in the human brain. Archives of General Psychiatry 1995;52(6):456‐63. [PUBMED: 7771915] - PubMed
Volkow 1998
Volkow 2002
-
- Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Logan J, Franceschi D, Maynard L, et al. Relationship between blockade of dopamine transporters by oral methylphenidate and the increases in extracellular dopamine: therapeutic implications. Synapse 2002;143(3):181‐7. [DOI: 10.1002/syn.10038; PUBMED: 11793423] - DOI - PubMed
Volkow 2003
Wang 2004
Ward 1993
Waxmonsky 2005
-
- Waxmonsky JG. Nonstimulant therapies for attention‐deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and adults. Essential Psychopharmacology 2005;6(5):262‐76. [PUBMED: 16222911] - PubMed
Weissman 1999
-
- Weissman MM. Social Adjustment Scale – Self‐report Technical Manual. Toronto (OT): Multi‐Health Systems, 1999.
Wender 2001
-
- Wender PH, Wolf LE, Wasserstein J. Adults with ADHD. An overview. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2001;931:1‐16. [PUBMED: 11462736] - PubMed
WHO 2011
-
- World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD‐10). Vol. 10th revision, WHO, 2010.
Wilens 2004
-
- Wilens TE, Dodson W. A clinical perspective of attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder into adulthood. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2004;65(10):1301‐13. [PUBMED: 15491232] - PubMed
Wilens 2006
-
- Wilens TE. Mechanism of action of agents used in attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2006;67(Suppl 8):32‐8. [PUBMED: 16961428] - PubMed
Wolraich 2004
-
- Wolraich ML, Doffing MA. Pharmacokinetic considerations in the treatment of attention‐deficit hyperactivity disorder with methylphenidate. CNS Drugs 2004;18(4):243‐50. [PUBMED: 15015904] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

