Neem oil nanoemulsions: characterisation and antioxidant activity
- PMID: 28965424
- PMCID: PMC6009939
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2017.1378190
Neem oil nanoemulsions: characterisation and antioxidant activity
Abstract
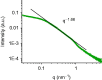
The aim of the present work is to develop nanoemulsions (NEs), nanosized emulsions, manufactured for improving the delivery of active pharmaceutical ingredients. In particular, nanoemulsions composed of Neem seed oil, contain rich bioactive components, and Tween 20 as nonionic surfactant were prepared. A mean droplet size ranging from 10 to 100 nm was obtained by modulating the oil/surfactant ratio. Physicochemical characterisation was carried out evaluating size, ζ-potential, microviscosity, polarity and turbidity of the external shell and morphology, along with stability in simulated cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), activity of Neem oil alone and in NEs, HEp-2 cell interaction and cytotoxicity studies. This study confirms the formation of NEs by Tween 20 and Neem oil at different weight ratios with small and homogenous dimensions. The antioxidant activity of Neem oil alone and in NEs was comparable, whereas its cytotoxicity was strongly reduced when loaded in NEs after interaction with HEp-2 cells.
Keywords: Neem oil; antioxidant activity; cell interaction studies; nanoemulsions; physicochemical characterisation.
Figures





References
-
- Divsalar A, Saboury AA, Nabiuni M, et al. . Characterization and side effect analysis of a newly designed nanoemulsion targeting human serum albumin for drug delivery. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2012;98:80–4. - PubMed
-
- Anton N, Benoit JP, Saulnier P.. Design and production of nanoparticles formulated from nano-emulsion templates – a review. J Control Release 2008;128:186–96. - PubMed
-
- Sharma N, Bansal M, Visht S, et al. . Nanoemulsion: a new concept of delivery system. Chron Young Sci 2010;1:2–4.
-
- Devarajan V, Ravichandran V.. Nanoemulsions: as modified drug delivery tool. Int J Compr Pharm 2011;2:1–5.
-
- Leite GM, Domingues RJ, Silva J, et al. . Antimicrobial effects of a microemulsion and a nanoemulsion on enteric and other pathogens and biofilms. Int J Food Microbiol 2007;118:15–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
