Temporal Control of Mammalian Cortical Neurogenesis by m6A Methylation
- PMID: 28965759
- PMCID: PMC5679435
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.003
Temporal Control of Mammalian Cortical Neurogenesis by m6A Methylation
Abstract
N6-methyladenosine (m6A), installed by the Mettl3/Mettl14 methyltransferase complex, is the most prevalent internal mRNA modification. Whether m6A regulates mammalian brain development is unknown. Here, we show that m6A depletion by Mettl14 knockout in embryonic mouse brains prolongs the cell cycle of radial glia cells and extends cortical neurogenesis into postnatal stages. m6A depletion by Mettl3 knockdown also leads to a prolonged cell cycle and maintenance of radial glia cells. m6A sequencing of embryonic mouse cortex reveals enrichment of mRNAs related to transcription factors, neurogenesis, the cell cycle, and neuronal differentiation, and m6A tagging promotes their decay. Further analysis uncovers previously unappreciated transcriptional prepatterning in cortical neural stem cells. m6A signaling also regulates human cortical neurogenesis in forebrain organoids. Comparison of m6A-mRNA landscapes between mouse and human cortical neurogenesis reveals enrichment of human-specific m6A tagging of transcripts related to brain-disorder risk genes. Our study identifies an epitranscriptomic mechanism in heightened transcriptional coordination during mammalian cortical neurogenesis.
Keywords: Mettl14; RNA methylation; autism; epitranscriptomics; human organoid; m(6)A; neurogenesis; radial glia cell; schizophrenia; transcriptional prepatterning.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
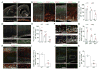
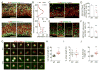
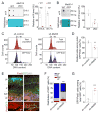
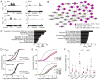
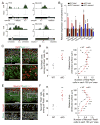
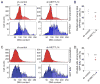
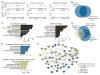
Comment in
-
Epimetronomics: m6A Marks the Tempo of Corticogenesis.Neuron. 2017 Nov 15;96(4):718-720. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.11.002. Neuron. 2017. PMID: 29144970
-
Layered-up regulation in the developing brain.Nature. 2017 Nov 23;551(7681):448-449. doi: 10.1038/d41586-017-07269-7. Nature. 2017. PMID: 29168827 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 NS097206/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 NS097370/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RM1 HG008935/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007814/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH087874/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007309/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007445/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS093772/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R33 MH087874/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK089502/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS047344/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 MH106434/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS095348/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS047344/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS048271/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS047344/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA043361/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS051630/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI131130/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008752/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH102690/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH105128/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

